Executive Summary: Why AI Automation Is Now a CFO-Level Priority
The conversation around artificial intelligence has shifted dramatically in boardrooms across America. What once lived in the realm of IT departments and innovation labs has now become a critical agenda item for CFOs and operations leaders. This isn't just another technology trend that will fade into obscurity. AI automation represents a fundamental shift in how businesses can achieve sustainable growth while maintaining operational excellence.
The numbers tell a compelling story. Companies implementing AI automation are seeing productivity gains of 30-70% in finance, compliance, and document-heavy processes. But these aren't just efficiency improvements. They're competitive advantages that separate market leaders from companies struggling to keep pace with rising operational costs and increasingly complex compliance demands.
Today's CFOs face unprecedented challenges. Labor costs continue to climb while margins face constant pressure. Regulatory requirements have become more data-intensive, demanding faster response times and greater accuracy. Market volatility requires real-time decision-making capabilities that traditional processes simply can't support. The role of the CFO has evolved from financial stewardship to strategic leadership, encompassing technology investments that drive operational transformation.
This transformation places CFOs in a unique position. As custodians of financial performance and operational efficiency, they're now the gatekeepers for technology ROI. Every automation initiative must demonstrate clear business value, measurable impact, and sustainable returns. The question isn't whether to adopt AI automation, but how to do it strategically and effectively.
The companies that succeed in this new landscape understand that AI automation isn't just a cost-saving lever. It's a value creation engine that can transform entire business operations. These leaders are moving beyond traditional automation approaches, embracing intelligent systems that don't just execute tasks but make decisions, validate data, and adapt to changing business conditions.
The strategic imperative is clear: CFOs and operations leaders who master AI automation today will define competitive advantage tomorrow. But success requires more than selecting the right technology. It demands a comprehensive approach that aligns stakeholders, mitigates risks, and scales systematically from pilot programs to enterprise-wide transformation.
Understanding the AI Automation Landscape in 2025
The automation landscape has undergone a dramatic evolution over the past few years. What began with simple robotic process automation (RPA) and optical character recognition (OCR) has transformed into sophisticated, intelligent systems capable of complex reasoning and decision-making. Understanding this evolution is crucial for CFOs and operations leaders evaluating their automation strategy.
Traditional automation tools were essentially digital workers that could replicate human actions on computer systems. They could click buttons, enter data, and move information between applications, but they couldn't think, reason, or adapt to new situations. These tools required extensive programming for each specific task and broke down whenever they encountered unexpected scenarios or data formats.
Modern AI automation platforms represent a quantum leap forward. Built on large language models (LLMs) and advanced machine learning algorithms, these systems can understand context, make intelligent decisions, and adapt to variations in data and processes. They don't just automate tasks; they orchestrate entire workflows with the kind of reasoning and flexibility that was previously exclusive to human workers.
The distinction becomes clear when examining document processing workflows. Legacy RPA systems could extract data from standardized forms with predefined templates, but they failed when document layouts changed or when dealing with unstructured content like emails, contracts, or financial reports. Today's AI automation platforms can analyze any document type, understand the content regardless of format, validate the information against business rules, and make intelligent decisions about next steps in the workflow.
This capability extends far beyond document processing. Modern AI automation can analyze market data to support pricing decisions, review contracts for compliance issues, validate financial data for accuracy and completeness, and even generate executive reports with insights and recommendations. These systems learn from patterns in historical data and can identify anomalies, trends, and opportunities that human analysts might miss.
For CFOs and operations leaders, this technological evolution addresses some of their most pressing challenges. The ability to process high volumes of complex, unstructured data with speed and accuracy directly impacts key performance indicators like Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), Days Payable Outstanding (DPO), and overall cycle times. More importantly, these systems provide real-time business intelligence that enables faster, more informed decision-making.
The compliance implications are equally significant. Modern AI automation platforms can be configured with complex business rules and regulatory requirements, ensuring that every transaction, document, and decision follows established protocols. They maintain detailed audit trails and can generate compliance reports automatically, reducing the risk of regulatory violations while minimizing the manual effort required for compliance management.
The scalability of these systems represents another major advancement. Where traditional automation required separate configurations for each process variation, modern AI platforms can handle diverse workflows within a single system. A platform like Artificio's Document Chat can process documents up to 500MB in size, handling everything from simple invoices to complex financial reports with equal sophistication.
This technological maturity has created a unique opportunity for forward-thinking CFOs. The combination of advanced capabilities, improved reliability, and proven ROI makes AI automation a strategic imperative rather than an experimental initiative. Companies that embrace these technologies now can establish significant competitive advantages while their peers continue to rely on manual processes and legacy automation tools.
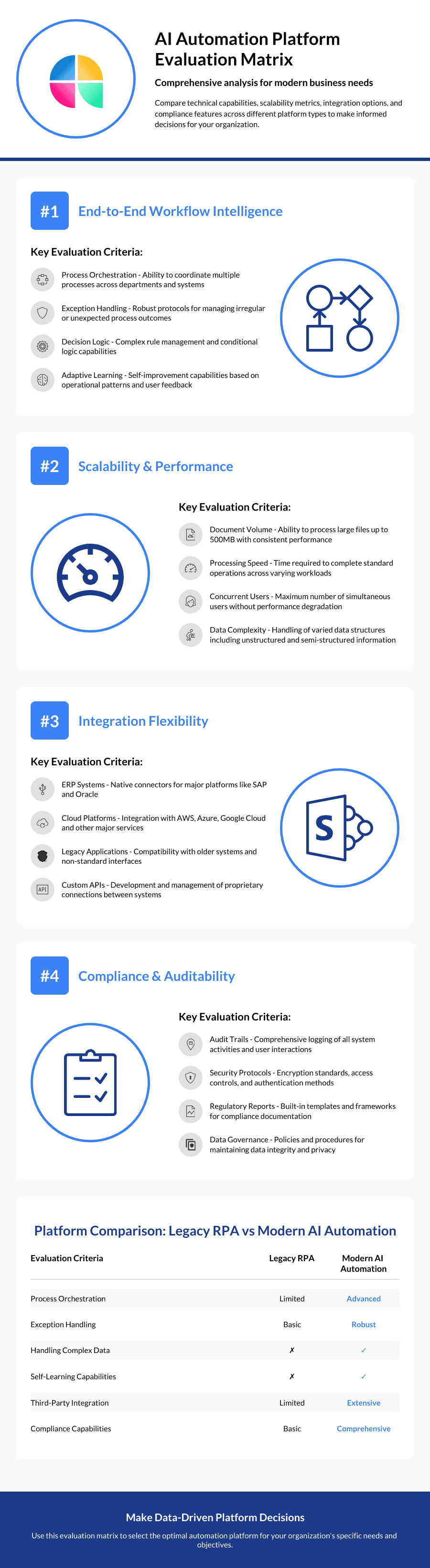
Decision Criteria: Evaluating AI Automation Platforms
Selecting the right AI automation platform requires a systematic evaluation approach that balances technical capabilities with business requirements. CFOs and operations leaders need a framework that assesses not just what a platform can do today, but how it will support long-term business objectives and adapt to evolving requirements.
Core Capabilities Assessment
The foundation of any evaluation should focus on end-to-end workflow intelligence. The best AI automation platforms don't just extract data from documents or automate individual tasks. They understand entire business processes and can orchestrate complex workflows that span multiple systems, departments, and decision points. This capability distinguishes true AI automation from enhanced RPA tools that simply perform tasks faster.
When evaluating platforms, examine how they handle exceptions and variations. Real business processes are messy and unpredictable. Invoices arrive in different formats, contracts contain unique terms, and financial data comes from various sources with different structures. The platform should demonstrate the ability to adapt to these variations without requiring extensive reprogramming or manual intervention.
Scalability represents another critical capability. Many automation platforms work well with small volumes of standardized data but struggle when faced with enterprise-level complexity. Look for platforms that can handle high-volume processing without degrading performance. The ability to process large documents, complex data structures, and multiple concurrent workflows indicates a platform built for enterprise deployment.
Integration flexibility cannot be overlooked in today's complex technology environment. Most organizations operate with a mixture of legacy systems, cloud applications, and modern platforms. The AI automation solution must seamlessly integrate with existing ERP systems like SAP and Oracle, customer relationship management platforms, document management systems, and industry-specific applications. The quality of these integrations often determines the success or failure of automation initiatives.
Compliance and auditability features have become non-negotiable for most organizations. The platform should provide transparent decision trails that show how conclusions were reached, what data was considered, and which business rules were applied. This transparency is essential for regulatory compliance, internal audits, and troubleshooting when issues arise. Look for platforms that can generate comprehensive audit reports and maintain detailed logs of all processing activities.
Financial Analysis Framework
From a financial perspective, the evaluation must consider both immediate costs and long-term value creation. The traditional CapEx versus OpEx analysis applies to AI automation, but the calculation is more complex than simple software licensing. Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes implementation services, training, ongoing support, and potential system modifications.
The projected savings calculation should be comprehensive and realistic. Don't limit the analysis to direct labor cost reductions. Factor in improvements to accuracy that reduce rework and compliance issues, faster cycle times that improve cash flow, and enhanced decision-making capabilities that drive revenue growth. These indirect benefits often exceed the direct cost savings and provide sustainable competitive advantages.
Key performance indicators should be clearly defined and measurable. Common metrics include processing time reduction, cost per transaction, error rate improvements, and compliance accuracy. But don't overlook strategic metrics like time to market for new products, customer satisfaction scores, and employee retention rates. AI automation often impacts these broader business outcomes in ways that aren't immediately obvious but create significant long-term value.
The payback period analysis should account for the learning curve and adoption timeline. Most AI automation implementations follow a gradual adoption curve, with initial deployments focused on specific use cases before expanding to broader applications. The financial model should reflect this phased approach and avoid unrealistic expectations about immediate full-scale benefits.
Vendor Assessment Strategy
Evaluating the vendor behind the platform is as important as assessing the technology itself. The AI automation market includes established enterprise software companies, innovative startups, and everything in between. Each type of vendor brings different strengths and risks that must be carefully considered.
Technology maturity should be evaluated through multiple lenses. How long has the vendor been developing AI automation solutions? What is their track record with enterprise implementations? Can they provide references from similar organizations facing comparable challenges? The answers to these questions provide insight into the vendor's ability to support your implementation and ongoing success.
Security capabilities require thorough investigation. The platform will likely process sensitive financial data, customer information, and proprietary business intelligence. Examine the vendor's security certifications, data encryption practices, access control mechanisms, and incident response procedures. Don't accept generic security statements; request detailed documentation and third-party security assessments.
The product roadmap reveals the vendor's strategic direction and commitment to continued innovation. AI automation is a rapidly evolving field, and platforms that don't innovate quickly become obsolete. Look for vendors with clear development priorities, regular product updates, and a vision that aligns with your long-term business objectives.
Implementation support and ongoing services often determine the difference between successful deployments and expensive failures. Evaluate the vendor's implementation methodology, training programs, and ongoing support capabilities. The best platforms are backed by teams that understand both the technology and the business processes it supports. They should provide comprehensive change management support, user training, and performance optimization services.
Stakeholder Alignment: Building a Cross-Functional Adoption Team
Successful AI automation adoption requires more than just selecting the right technology platform. It demands careful orchestration of stakeholders across the organization, each bringing unique perspectives and requirements that must be balanced and aligned. The CFO's leadership role in this process extends beyond financial oversight to become the central coordinator ensuring that all voices are heard and incorporated into the adoption strategy.
The CFO's position as both financial steward and strategic leader makes them uniquely qualified to lead AI automation initiatives. Unlike IT-led technology projects that may lack business context, or operations-led efficiency programs that may not consider financial implications, CFO-led automation initiatives naturally balance technical capabilities with business value. This leadership approach ensures that automation investments align with broader business objectives and deliver measurable returns.
Building an effective adoption team requires identifying stakeholders who will be impacted by automation and those who can influence its success. The core team typically includes the CFO providing financial oversight and ROI measurement, the COO or operations leader ensuring workflow integration and process optimization, the CIO or CTO addressing data security and system integration requirements, and business unit leaders who own the processes being automated.
Each stakeholder brings critical perspectives that must be incorporated into the adoption strategy. Operations leaders understand the nuances of existing workflows, the pain points that automation should address, and the practical considerations that determine whether new processes will be adopted by front-line workers. They can identify the highest-impact opportunities for automation and help design solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing operations.
IT leadership provides essential technical expertise around system integration, data security, and infrastructure requirements. Their involvement ensures that automation platforms are implemented according to enterprise standards and don't create security vulnerabilities or system compatibility issues. They also provide realistic assessments of implementation timelines and technical complexity.
Business unit leaders who own the processes being automated serve as crucial advocates and change agents within their teams. Their support is essential for user adoption and ongoing success. These leaders can provide detailed process knowledge, help identify potential obstacles to adoption, and serve as champions who encourage their teams to embrace new ways of working.
The communication strategy for stakeholder alignment must translate technical capabilities into business outcomes that resonate with each audience. For operations teams, focus on how automation will eliminate repetitive tasks and enable them to focus on higher-value activities. For IT teams, emphasize the platform's security features, integration capabilities, and scalability. For business unit leaders, highlight specific improvements to metrics they care about, such as reduced processing times, improved accuracy, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
One effective approach is to develop specific use case scenarios that demonstrate how automation will impact each stakeholder's daily work. For example, describe how automated invoice processing will reduce the accounts payable team's manual workload while providing the CFO with real-time visibility into cash flow obligations and giving the operations leader better predictability in payment cycles.
Regular communication and feedback loops are essential throughout the adoption process. Establish recurring meetings where stakeholders can share progress updates, identify challenges, and collaborate on solutions. Create channels for ongoing feedback that allow team members to raise concerns and suggest improvements. This collaborative approach builds buy-in and ensures that the automation solution evolves to meet the organization's changing needs.
Success metrics should be defined collaboratively, with each stakeholder contributing metrics that matter to their area of responsibility. Financial metrics like cost savings and ROI satisfy the CFO's requirements, while operational metrics like processing time and error rates address operations leaders' concerns. IT metrics around system uptime and security incidents ensure technical success. This comprehensive measurement approach provides a complete picture of automation impact and helps identify areas for improvement.
Integration Concerns and Risk Mitigation
The complexity of modern enterprise technology environments creates significant challenges for AI automation implementation. Most organizations operate with a mixture of legacy systems, cloud-based applications, and modern platforms that weren't designed to work together seamlessly. Successfully integrating AI automation into this environment requires careful planning, risk assessment, and mitigation strategies that address both technical and operational concerns.
Legacy system compatibility represents one of the most common obstacles to automation success. Many organizations rely on ERP systems, financial applications, and business-critical databases that were implemented years or even decades ago. These systems often lack modern APIs, use proprietary data formats, or have technical limitations that complicate integration efforts. The temptation to pursue "rip and replace" strategies can be overwhelming, but this approach typically involves prohibitive costs, extended implementation timelines, and significant business disruption.
A more practical approach focuses on building integration layers that connect AI automation platforms with existing systems without requiring major modifications. Modern automation platforms include pre-built connectors for popular enterprise applications and flexible integration capabilities that can accommodate custom interfaces. This approach allows organizations to leverage their existing technology investments while adding intelligent automation capabilities.
The integration strategy should prioritize systems that handle the highest volume of transactions or contain the most critical business data. Start with integrations that provide immediate value and build confidence in the platform's capabilities. These early wins create momentum for more complex integrations and help justify continued investment in the automation program.
Data privacy and security concerns have become increasingly important as organizations handle larger volumes of sensitive information and face stricter regulatory requirements. AI automation platforms typically process financial data, customer information, and proprietary business intelligence that requires the highest levels of protection. The security strategy must address data encryption, access controls, audit logging, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Encryption should protect data both in transit and at rest. Look for platforms that use enterprise-grade encryption standards and provide detailed documentation about their security architectures. Access controls should follow the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users can only access the data and functions necessary for their specific roles. Role-based access control systems should integrate with existing identity management platforms to maintain consistent security policies across the organization.
Audit logging capabilities are essential for compliance and troubleshooting. The platform should maintain detailed records of all processing activities, including who accessed what data, when processing occurred, and what decisions were made. These logs should be tamper-evident and stored in a format that supports compliance reporting and forensic analysis when necessary.
Change management often determines the success or failure of automation initiatives more than technical factors. Even the most sophisticated automation platform will fail if users don't adopt it or if existing processes aren't properly redesigned to take advantage of new capabilities. The change management strategy should address both the technical aspects of implementation and the human factors that influence adoption.
User training programs should go beyond basic platform functionality to include the business rationale for automation, the benefits it provides to individual workers, and the ways it will change their daily responsibilities. Many employees fear that automation will eliminate their jobs, so the training program should clearly explain how automation will enhance their capabilities and enable them to focus on more strategic, value-added activities.
Communication throughout the implementation process should be transparent and regular. Keep stakeholders informed about progress, challenges, and successes. Address concerns promptly and provide forums where employees can ask questions and provide feedback. This open communication approach builds trust and encourages adoption.
The pilot approach to implementation provides an effective risk mitigation strategy that allows organizations to validate assumptions, refine processes, and build confidence before committing to full-scale deployment. A well-designed pilot program focuses on a specific use case with clearly defined success criteria and measurable outcomes. This approach allows organizations to learn from experience and make adjustments before expanding automation to additional processes.
Pilot selection should balance potential impact with implementation complexity. Choose processes that are important enough to demonstrate clear value but straightforward enough to implement successfully. Avoid pilots that depend on complex integrations or require significant process redesign. The goal is to prove the platform's capabilities and build organizational confidence in automation.
Success metrics for the pilot should be specific, measurable, and time-bound. Define baseline measurements for key performance indicators before implementation begins, and establish regular checkpoints to assess progress. Document lessons learned throughout the pilot and use these insights to improve the approach for subsequent implementations.
Pilot to Scale: A Practical Adoption Roadmap
Transforming AI automation from a promising concept to enterprise-wide reality requires a systematic approach that builds capability and confidence progressively. The most successful implementations follow a structured roadmap that begins with carefully selected pilot projects and scales systematically to comprehensive automation programs. This approach minimizes risk while maximizing learning and organizational buy-in.
Step 1: Strategic Process Selection
The foundation of successful AI automation adoption lies in selecting the right initial processes for automation. This decision has cascading effects on everything from technical implementation to organizational acceptance. The ideal pilot process combines high business impact with manageable implementation complexity, creating conditions for early success that builds momentum for broader adoption.
High-impact processes typically involve significant manual effort, frequent errors, or time-sensitive requirements that affect business performance. Accounts payable automation represents a classic example, where manual invoice processing creates bottlenecks that affect supplier relationships and cash flow management. Claims validation in insurance companies offers another compelling opportunity, where faster, more accurate processing directly impacts customer satisfaction and operational costs.
The assessment should also consider process standardization and data availability. Processes with well-defined steps and consistent data formats are easier to automate and more likely to deliver predictable results. Avoid processes that require extensive customization or depend on tribal knowledge that hasn't been documented. These complexities can derail pilot programs and create negative perceptions about automation capabilities.
Contract review and analysis presents an interesting middle ground. While contracts contain unstructured data and require sophisticated analysis, the potential business impact is substantial. Modern AI platforms can analyze contract terms, identify compliance issues, and flag unusual provisions with accuracy that often exceeds human reviewers. The key is starting with contract types that follow standard formats and gradually expanding to more complex agreements.
Step 2: Defining Success Through Measurement
Clear, measurable success criteria transform subjective impressions into objective business results. The metrics selected for the pilot program should align with broader business objectives while providing specific, actionable insights about automation performance. These measurements serve multiple purposes: they validate the business case for automation, identify areas for improvement, and provide benchmarks for scaling decisions.
Processing time represents the most straightforward and immediately visible metric. Document the current time required for manual processing and compare it to automated processing times. But don't stop at simple time measurements. Break down the analysis to understand where time savings occur and identify any new bottlenecks that automation might create. For example, while AI might process invoices in minutes instead of hours, approval workflows might still require human intervention that limits overall cycle time improvements.
Cost per document or transaction provides clear financial metrics that CFOs can easily evaluate and compare to other business investments. This calculation should include both direct labor costs and indirect expenses like error correction, rework, and compliance management. Many organizations discover that the indirect costs of manual processes far exceed the direct labor expenses, making automation ROI even more compelling than initially projected.
Error rates and quality measurements demonstrate automation's impact on accuracy and compliance. Establish baseline error rates for manual processes and track how automation affects different types of errors. Some errors might be eliminated entirely, while others might shift to different parts of the process. Understanding these patterns helps optimize both the automation configuration and the surrounding workflows.
Customer or stakeholder satisfaction metrics capture the broader business impact of process improvements. Faster invoice processing might improve supplier satisfaction scores, while more accurate claims processing could enhance customer experience ratings. These broader metrics help justify automation investments beyond simple cost reduction and demonstrate strategic value creation.
Step 3: Pilot Implementation Excellence
The pilot implementation phase tests not just the technology platform but the organization's readiness for change. Success depends on careful project management, stakeholder engagement, and systematic problem-solving when challenges arise. The goal is to create a learning environment that validates assumptions while building organizational capability for larger-scale implementations.
Project scope should be tightly controlled to ensure focus and measurability. Define specific document types, transaction volumes, and processing requirements that the pilot will address. Resist the temptation to expand scope during implementation, as this often leads to delays and confused results. Document any scope changes and their rationale for future reference.
User engagement during the pilot is crucial for long-term success. Include the people who will ultimately use the system in design decisions and testing activities. Their practical knowledge about process variations and exception handling helps create more robust automation solutions. Their involvement also builds the advocacy network that will support broader adoption.
Data quality issues often emerge during pilot implementation and can derail progress if not addressed systematically. Establish clear data quality standards and implement validation procedures that identify and resolve issues quickly. Many organizations discover that automation initiatives drive improvements in data management practices that benefit the entire organization.
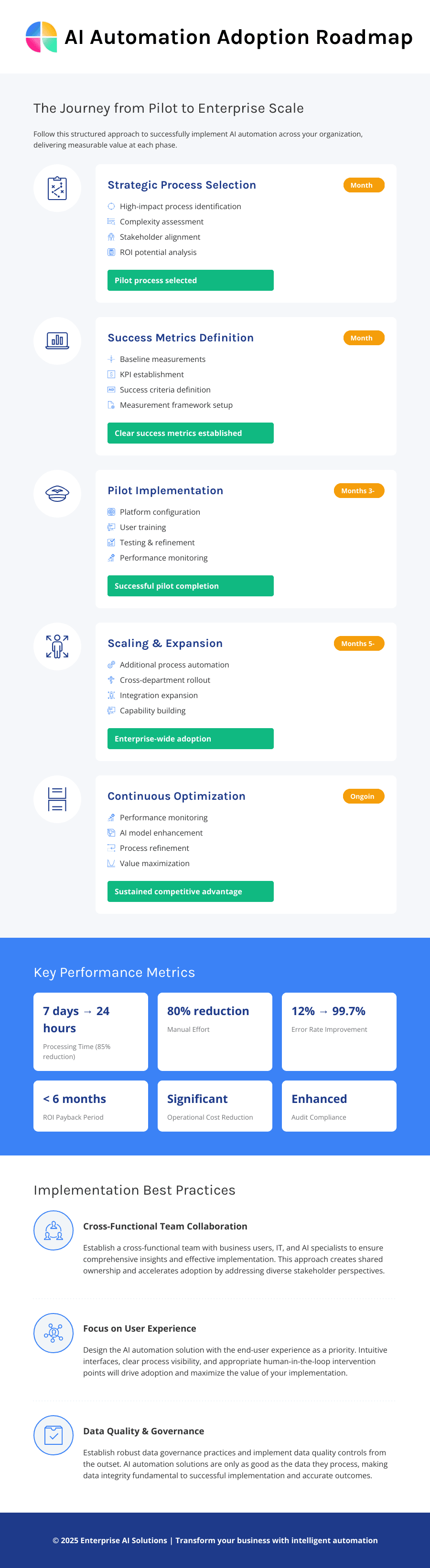
Step 4: Scaling Strategy and Expansion
Successful pilot programs create the foundation for systematic expansion to additional processes and business units. The scaling strategy should leverage lessons learned during the pilot while addressing the increased complexity that comes with broader deployment. This phase transforms automation from a departmental efficiency tool to an enterprise capability that drives competitive advantage.
Process prioritization for scaling should consider both business impact and implementation complexity. Create a portfolio of potential automation opportunities and evaluate each based on expected ROI, technical requirements, and organizational readiness. This portfolio approach allows for balanced expansion that delivers quick wins while building capability for more complex implementations.
The expansion strategy should also consider interdependencies between processes. Some automation opportunities become more valuable when implemented together, while others might conflict or create unnecessary complexity. Map these relationships and plan implementation sequences that maximize synergies and minimize disruptions.
Technology platform scalability becomes critical as automation expands beyond initial use cases. Evaluate whether the chosen platform can handle increased processing volumes, additional document types, and more complex workflows. Plan for infrastructure upgrades and additional licensing as automation adoption grows.
Organizational capability development must keep pace with technology deployment. Expand training programs, develop internal expertise, and create support structures that can handle a larger automation footprint. Consider establishing a center of excellence that can provide guidance, best practices, and technical support for business units implementing automation.
Step 5: Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Automation is not a "set it and forget it" technology. The most successful implementations include ongoing monitoring, optimization, and enhancement processes that ensure continued value creation and adapt to changing business requirements. This continuous improvement approach maximizes ROI and maintains competitive advantages over time.
Performance monitoring should track both technical metrics and business outcomes on an ongoing basis. Automated dashboards can provide real-time visibility into processing volumes, error rates, and performance trends. Regular business reviews should assess whether automation continues to deliver expected benefits and identify opportunities for improvement.
AI model enhancement represents a unique opportunity in modern automation platforms. Unlike traditional automation tools that perform the same tasks indefinitely, AI-powered systems can learn from new data and improve their performance over time. Establish processes for incorporating feedback, retraining models, and deploying improvements systematically.
Process evolution should be expected and planned for. Business requirements change, regulatory environments evolve, and technology capabilities advance. Build flexibility into automation solutions that allows for modifications and enhancements without requiring complete reimplementation.
Success stories and lessons learned should be documented and shared across the organization. These case studies provide valuable guidance for future implementations and help build organizational enthusiasm for automation. They also serve as important inputs for business case development when evaluating additional automation investments.
Case Snapshot: CFO-Led AI Transformation with Artificio
The theoretical benefits of AI automation become tangible when examined through real-world implementation stories. Consider the transformation journey of a mid-sized financial services company whose CFO recognized that manual accounts payable processes were constraining growth and creating unnecessary operational risk. This case demonstrates how strategic leadership, systematic implementation, and the right technology platform can deliver transformational results in months rather than years.
The company faced challenges that many CFOs will recognize immediately. Their accounts payable team was processing over 5,000 invoices monthly using a combination of email, paper documents, and spreadsheet-based tracking systems. The manual process required seven business days on average to move an invoice from receipt to approval, with additional delays when invoices contained discrepancies or required special handling. Error rates averaged 12%, leading to supplier disputes, duplicate payments, and compliance issues that consumed additional resources to resolve.
The CFO's analysis revealed that these inefficiencies were creating cascading business impacts beyond simple processing costs. Extended payment cycles strained supplier relationships and sometimes resulted in missed early payment discounts that could have improved cash flow. The manual tracking systems provided limited visibility into pending payments, making cash flow forecasting and working capital management more difficult. Perhaps most concerning, the error-prone manual process created audit risks and potential compliance violations that could have serious regulatory implications.
The decision to implement Artificio's AI automation platform emerged from a comprehensive evaluation process that considered multiple vendors and approaches. The CFO's assessment focused on the platform's ability to handle the full spectrum of invoice types and formats the company received, from simple purchase order invoices to complex service agreements with variable pricing structures. The evaluation also prioritized integration capabilities with their existing ERP system and the ability to maintain detailed audit trails for compliance purposes.
Implementation began with a carefully scoped pilot program focused on standard purchase order invoices, which represented about 60% of their total invoice volume. The pilot included 500 invoices over a one-month period, with success metrics defined around processing time, accuracy, and user satisfaction. The Artificio platform was configured to extract invoice data, validate it against purchase order information, apply approval workflows based on dollar amounts and GL codes, and integrate with their ERP system for final posting.
The pilot results exceeded expectations across all measured categories. Processing time for the pilot invoices averaged 4 hours from receipt to approval, representing an 85% reduction from the previous 7-day cycle. Accuracy improved dramatically, with error rates dropping to less than 2% for the automated invoices. User satisfaction scores from the accounts payable team were overwhelmingly positive, with team members appreciating the elimination of repetitive data entry and the ability to focus on exception handling and vendor relationship management.
Building on the pilot success, the company expanded automation to additional invoice types over the following three months. The implementation team worked systematically through service invoices, utility bills, and professional services agreements, refining the automation rules and workflows for each category. The Artificio platform's machine learning capabilities allowed it to improve accuracy and handling for each new invoice type based on historical patterns and user feedback.
The financial impact became clear within six months of full implementation. Manual effort in accounts payable was reduced by 80%, allowing the company to reallocate two full-time employees to higher-value financial analysis activities instead of hiring additional staff to handle growing invoice volumes. Processing cycle time stabilized at 24 hours for 95% of invoices, with complex or exception invoices requiring an additional 24-48 hours for resolution.
Compliance accuracy reached 99.7%, with automated audit trails and approval documentation that exceeded their previous manual capabilities. The improved accuracy eliminated virtually all duplicate payments and reduced supplier disputes by 90%. Early payment discount capture improved by 40% due to faster processing and better cash flow visibility.
The payback period for the automation investment was less than six months, driven primarily by labor cost reductions and improved cash flow management. The strategic benefits extended beyond simple cost savings, with improved vendor relationships, better cash flow forecasting, and enhanced audit capabilities that provided ongoing value. The accounts payable team transformed from transaction processors to business partners who could focus on supplier negotiations, process improvement, and financial analysis.
The success of the accounts payable automation project created momentum for additional automation initiatives across the organization. The CFO leveraged the demonstrated ROI and organizational buy-in to expand automation to expense management, contract analysis, and financial reporting processes. Each subsequent implementation benefited from the lessons learned and organizational capability developed during the initial project.
This case demonstrates several critical success factors for CFO-led automation initiatives. The systematic approach to vendor evaluation and pilot implementation minimized risks while building organizational confidence. The focus on measurable business outcomes rather than just technology capabilities ensured that the project delivered real value. The CFO's leadership in driving change management and stakeholder alignment created conditions for successful adoption and scaling.
Conclusion: From Cost Control to Strategic Value Creation
The transformation of AI automation from experimental technology to business imperative represents a pivotal moment for CFOs and operations leaders. Organizations that recognize this shift and act decisively will establish competitive advantages that extend far beyond simple cost reduction. The strategic value of AI automation lies not just in its ability to eliminate manual tasks, but in its capacity to fundamentally reimagine how businesses operate, make decisions, and create value for stakeholders.
The evolution from cost control to strategic value creation requires a fundamental shift in how CFOs approach automation investments. Traditional cost-cutting initiatives focus on reducing expenses and improving efficiency within existing processes. While these benefits remain important, they represent only the foundation of automation's true potential. The strategic value emerges when automation enables new business capabilities, accelerates decision-making, and creates competitive differentiators that drive revenue growth and market expansion.
Forward-thinking CFOs are discovering that AI automation can transform their role from financial steward to strategic architect. The real-time visibility into business operations that automation provides enables more accurate forecasting, faster response to market changes, and better resource allocation decisions. The elimination of manual, error-prone processes reduces operational risk and improves compliance, but it also frees up human resources to focus on analysis, strategy, and innovation activities that drive business growth.
The compounding effects of automation adoption create increasing returns over time. Early implementations build organizational capability and confidence that accelerates subsequent projects. The data generated by automated processes provides insights that improve decision-making across the organization. The efficiency gains create capacity for new initiatives and market expansion that wouldn't have been possible with manual processes.
Operations leaders who embrace this transformation discover that automation doesn't just make existing processes faster and more accurate. It enables entirely new approaches to business operations that weren't feasible with manual processes. Real-time processing of complex data, predictive analytics for demand planning, and automated compliance monitoring represent new operational capabilities that create sustainable competitive advantages.
The technology landscape supporting this transformation continues to evolve rapidly, with platforms like Artificio leading the development of intelligent automation solutions that go beyond traditional RPA to provide true business intelligence and decision-making capabilities. These advanced platforms offer the scalability, flexibility, and sophistication required for enterprise-wide transformation initiatives.
The window of opportunity for gaining competitive advantage through AI automation won't remain open indefinitely. As these technologies become more widely adopted, the benefits will shift from competitive differentiators to table stakes for business operation. CFOs and operations leaders who act now can establish positions of strength that will be difficult for competitors to match.
The strategic imperative is clear: organizations that master AI automation will define the future of business operations. Those that continue to rely on manual processes and legacy systems will find themselves at increasing disadvantage in terms of cost structure, operational agility, and decision-making speed. The question is not whether to adopt AI automation, but how quickly and effectively it can be implemented to drive strategic value creation.
Success in this transformation requires more than selecting the right technology platform. It demands strategic leadership that can align stakeholders, manage change, and execute systematically from pilot programs to enterprise-wide adoption. CFOs who provide this leadership will transform their organizations and establish themselves as strategic value architects who drive sustainable competitive advantage through intelligent automation.
The future belongs to organizations that can combine human insight with artificial intelligence to create new levels of operational excellence and strategic capability. Artificio provides the platform and capabilities needed to execute this vision today, but success ultimately depends on the leadership, strategy, and execution that CFOs and operations leaders bring to the transformation process.
The time for incremental improvement has passed. The organizations that thrive in the coming decade will be those that embrace AI automation as a strategic imperative and execute comprehensive transformation initiatives that create lasting competitive advantages. The tools, technologies, and methodologies exist today. The only remaining question is which leaders will seize this opportunity to transform their organizations and define the future of their industries.
