The business world runs on decisions. Every invoice needs approval, every loan application requires evaluation, and every contract must be validated against company policies. For decades, organizations have relied on automation to streamline these processes, but traditional systems hit a wall when it comes to the nuanced, context-dependent decisions that drive real business value.
Most automation tools excel at extracting data from documents. They can pull invoice amounts, identify customer names, and capture contract dates with impressive accuracy. But extracting data is just the first step. The real challenge lies in what happens next: applying complex business rules, understanding context, and making intelligent decisions based on that information.
This gap between data extraction and decision-making has created a bottleneck in countless organizations. Teams find themselves manually reviewing documents that their automation systems have already processed, applying rules that should be automated but remain stubbornly manual. The result is workflows that are only partially automated, requiring human intervention at precisely the points where automation would deliver the most value.
LLM-powered rules engines represent a fundamental shift in how we approach business automation. These systems don't just read data they understand it, interpret it within context, and apply sophisticated rules to make the kinds of decisions that previously required human judgment. By combining the pattern recognition capabilities of large language models with the reliability of structured rule systems, they bridge the gap between simple data extraction and intelligent business process automation.
The Evolution from Static to Intelligent Rule Systems
Traditional rule engines operate on a straightforward principle: if condition X is met, then perform action Y. These static systems have served businesses well for routine, predictable scenarios. A simple example might be routing invoices over $10,000 to the CFO for approval, or flagging expense reports that exceed daily limits. These rules work perfectly when business conditions are stable and exceptions are rare.
The limitations of static rule engines become apparent when businesses need to handle complex, context-dependent scenarios. Consider a contract review process where the rules aren't just about dollar amounts or dates, but about interpreting language, understanding regulatory requirements, and assessing risk based on multiple interrelated factors. A static rule might flag contracts with certain keywords, but it can't understand whether a liability clause is reasonable given the specific context of the agreement.
Static engines also struggle with adaptability. When regulations change, market conditions shift, or business priorities evolve, each rule must be manually updated by developers or IT teams. This process is time-consuming, error-prone, and often creates delays that impact business operations. The result is systems that lag behind business needs, requiring constant maintenance and failing to capture the full value of automation.
LLM-powered rules engines operate on an entirely different principle. Instead of relying on hardcoded conditions, they interpret rules written in natural language and apply them contextually to each document or transaction. These systems can understand complex instructions like "approve loans where the applicant has stable employment, reasonable debt-to-income ratio, and no recent credit issues, but consider industry-specific risks for hospitality and retail sectors."
The intelligence in these systems comes from their ability to reason about information the same way humans do. They can weigh multiple factors, consider exceptions, and make nuanced decisions based on context. When a rule mentions "stable employment," the system understands that this means different things for a teacher versus a freelance consultant, and it can adjust its evaluation accordingly.
Perhaps most importantly, LLM-powered engines can evolve with changing business needs. Rules can be updated in natural language without requiring code changes, and the system can learn from historical decisions to improve its accuracy over time. This adaptability means businesses can respond quickly to new opportunities, regulatory changes, or market conditions without lengthy development cycles.
Transforming Finance Operations Through Intelligent Automation
Financial services organizations process enormous volumes of documents and transactions that require sophisticated decision-making. From loan applications to investment approvals, from compliance checks to fraud detection, finance teams make thousands of rule-based decisions every day. Many of these decisions involve complex criteria that traditional automation systems struggle to handle effectively.
Loan approval processes exemplify the complexity that LLM-powered rules engines can address. A typical loan application involves multiple data points: credit scores, income verification, employment history, debt obligations, and collateral assessments. Traditional systems might apply rigid score-based rules, but they often miss nuances that human underwriters would catch. An applicant might have a temporary dip in credit score due to medical expenses, or their income might be irregular due to commission-based compensation.
LLM-powered rules engines can evaluate loan applications with the same contextual understanding that experienced underwriters bring to their work. They can recognize that a freelance graphic designer with three years of consistent client relationships represents a different risk profile than someone with gaps in employment history. They can weigh positive factors like increasing income trends against negative factors like recent credit inquiries, creating a holistic assessment that goes beyond simple numerical thresholds.
Risk assessment and fraud detection represent another area where intelligent rules engines excel. Financial crimes have become increasingly sophisticated, and fraudsters constantly evolve their tactics to avoid detection by traditional rule-based systems. Static rules that flag specific transaction patterns quickly become obsolete as criminals adapt their methods. 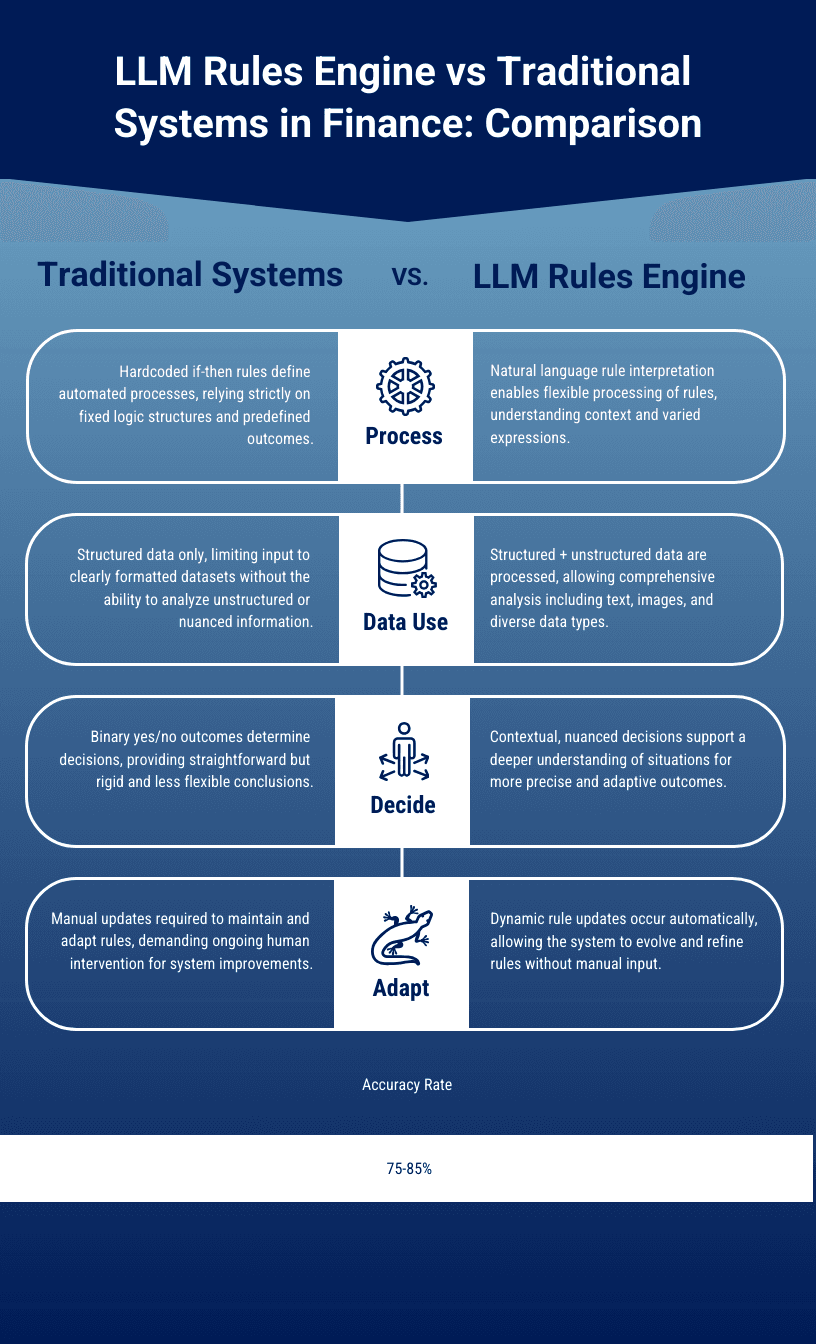
LLM-powered systems can identify suspicious patterns that haven't been seen before by understanding the underlying behaviors that indicate fraud risk. They can analyze transaction narratives, assess the reasonableness of business expenses, and detect inconsistencies in documentation that might indicate fraudulent activity. More importantly, they can adapt their detection methods as new fraud patterns emerge, maintaining effectiveness without requiring constant rule updates.
Regulatory compliance presents ongoing challenges for financial institutions, as rules and requirements change frequently and often involve complex interpretations. KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) requirements vary by jurisdiction and transaction type, creating a web of rules that's difficult to manage with traditional systems.
Intelligent rules engines can interpret regulatory requirements written in natural language and apply them consistently across different types of transactions and customer profiles. When regulations change, compliance teams can update rules by describing the new requirements in plain English, rather than waiting for developers to modify code. This capability dramatically reduces the time between regulatory changes and implementation, helping organizations maintain compliance while minimizing operational disruption.
Invoice processing and accounts payable automation showcase how LLM-powered rules can handle the exceptions and edge cases that plague traditional systems. While extracting basic invoice information is straightforward, determining whether to approve payment often involves complex business logic. Factors might include vendor relationships, budget approvals, contract terms, and company policies that vary by department or project type.
An intelligent rules engine can evaluate invoices against multiple criteria simultaneously, understanding context like project codes, approval hierarchies, and vendor agreements. It can recognize when an invoice amount slightly exceeds a purchase order due to legitimate shipping charges versus potential billing errors. It can route invoices through appropriate approval workflows based on the combination of amount, vendor type, and business unit requirements, handling the complexity that often forces organizations to rely on manual processing.
Revolutionizing Legal Document Processing and Contract Management
Legal operations present some of the most complex rule-based decision-making scenarios in business. Contract reviews, compliance assessments, and risk evaluations require deep understanding of language, context, and implications that go far beyond simple data extraction. Legal professionals spend countless hours reviewing documents for specific clauses, comparing terms against standard templates, and assessing risks based on nuanced language and business context.
Contract validation represents a prime use case for LLM-powered rules engines. Legal teams typically maintain detailed guidelines about acceptable contract terms, required clauses, and red-flag provisions that require special attention. Traditional systems might flag contracts containing certain keywords, but they can't evaluate whether liability limitations are reasonable, whether termination clauses provide adequate protection, or whether confidentiality provisions meet company standards.
Intelligent rules engines can read contract language with the same comprehension that human reviewers bring to their work. They can understand that a limitation of liability clause isn't just about finding the words "limitation of liability," but about evaluating whether the specific limitations are appropriate for the type of agreement, the business relationship, and the potential risks involved. They can recognize when indemnification language is one-sided and flag agreements that don't meet company standards for risk allocation.
The ability to compare contracts against template language represents another significant advancement. Rather than simple word matching, LLM-powered systems can understand when contract provisions accomplish the same goals using different language. They can recognize that "either party may terminate this agreement with thirty days written notice" and "this agreement may be terminated by either party upon thirty days advance written notification" express the same concept, even though the exact wording differs.
Due diligence processes in mergers and acquisitions showcase the power of intelligent document analysis. Legal teams reviewing hundreds or thousands of contracts need to identify potential risks, unusual terms, and compliance issues across diverse document types. Traditional systems might categorize documents or extract basic information, but they can't assess the business implications of specific contract provisions.
LLM-powered rules engines can analyze contracts for factors like change of control provisions that might be triggered by the transaction, unusual warranty or representation language that could create unexpected liabilities, or termination rights that might be exercised post-acquisition. They can provide summaries that highlight the business implications of legal language, helping deal teams understand potential risks without requiring legal experts to review every document in detail.
Regulatory compliance in legal operations often involves interpreting complex requirements and applying them across different types of agreements and business relationships. Privacy regulations like GDPR, industry-specific requirements, and jurisdictional variations create a complex web of compliance obligations that traditional rule-based systems struggle to manage effectively.
Intelligent systems can interpret regulatory requirements and identify relevant contract provisions automatically. They can recognize when data processing clauses might conflict with privacy regulations, when cross-border data transfer provisions need additional safeguards, or when retention periods exceed regulatory limits. As regulations change, legal teams can update compliance rules by describing new requirements in natural language, rather than waiting for technical implementations.
Contract lifecycle management benefits significantly from intelligent automation throughout the entire process, from initial drafting through renewal or termination. Rules engines can route contracts through appropriate approval workflows based on risk assessment, business impact, and company policies. They can identify contracts approaching expiration dates and flag those requiring action, understanding the business context that determines whether renewal, renegotiation, or termination is appropriate.
The system can also learn from historical decisions to improve future recommendations. By analyzing patterns in past contract reviews, risk assessments, and business outcomes, intelligent rules engines can develop increasingly sophisticated understanding of what constitutes acceptable risk for different types of agreements and business relationships.
Optimizing Supply Chain and Manufacturing Operations
Supply chain and manufacturing operations depend on complex networks of vendors, contracts, and compliance requirements that generate constant streams of documentation requiring review and decision-making. Purchase orders, vendor certifications, quality reports, and compliance documentation all require evaluation against business rules that are often nuanced and context-dependent.
Purchase order validation exemplifies the complexity that intelligent rules engines can address effectively. While traditional systems might verify that PO amounts don't exceed budget limits, real-world approval processes involve much more sophisticated logic. Factors might include vendor performance history, strategic importance of purchases, alternative sourcing options, and market conditions that affect pricing or availability.
LLM-powered rules engines can evaluate purchase orders against multiple criteria simultaneously, understanding business context that traditional systems miss. They can recognize when pricing variations are justified by market conditions versus potential supplier issues. They can assess whether delivery timelines are reasonable given current supply chain conditions and flag orders that might impact production schedules.
The system can also understand relationships between different purchase orders and business requirements. For example, it might recognize that rush orders for raw materials suggest potential production issues that require management attention, or that changes in supplier mix indicate strategic shifts that need coordination across departments. 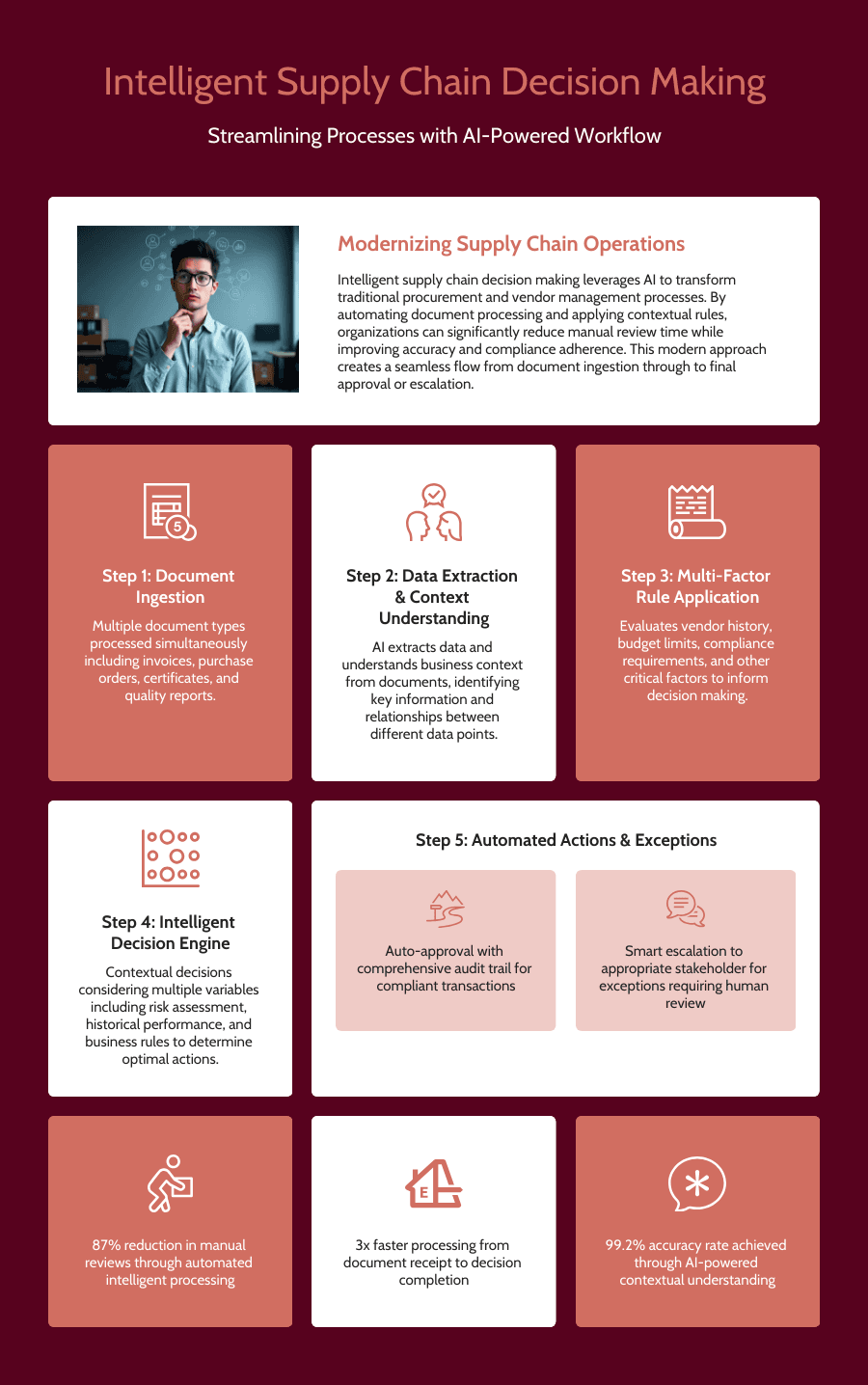
Vendor compliance and certification management represents another area where intelligent automation delivers significant value. Manufacturing organizations must verify that suppliers meet quality standards, maintain required certifications, and comply with regulatory requirements. Traditional systems might track certification expiration dates, but they can't evaluate whether vendor performance meets quality standards or assess risks associated with supplier changes.
Intelligent rules engines can analyze vendor performance data, quality reports, and certification documents to provide comprehensive supplier assessments. They can identify trends that suggest quality issues before they impact production, recognize when vendor changes require additional oversight, and flag potential compliance risks based on regulatory requirements and business policies.
Quality control processes benefit from intelligent analysis of inspection reports, test results, and customer feedback. Rather than simply flagging values outside specified ranges, LLM-powered systems can understand the business implications of quality variations and recommend appropriate responses. They can recognize patterns that suggest systemic issues versus random variations, helping quality teams focus their attention where it can have the greatest impact.
Exception handling in supply chain operations showcases the adaptability that intelligent rules engines bring to business processes. Supply chains face constant disruptions from weather, transportation issues, supplier problems, and market changes. Traditional systems often escalate exceptions to human operators, but intelligent systems can evaluate exceptions against business priorities and recommend appropriate responses.
For example, when a supplier reports delivery delays, an intelligent system can assess the impact on production schedules, evaluate alternative sourcing options, and recommend whether to expedite shipping, find alternative suppliers, or adjust production plans. The system can understand trade-offs between cost, quality, and delivery timing, providing recommendations that align with current business priorities.
Inventory management decisions often require balancing multiple competing factors including carrying costs, stockout risks, supplier lead times, and demand forecasts. Intelligent rules engines can evaluate these factors holistically, understanding that optimal inventory levels depend on current business conditions, not just historical patterns. They can recognize when inventory buildup indicates potential demand issues versus prudent risk management, and adjust recommendations accordingly.
Artificio's Advanced Rules Module: Engineering Accuracy Through Multi-Agent Intelligence
The effectiveness of any rules engine depends on its ability to make accurate decisions consistently, provide clear rationale for those decisions, and adapt to changing business requirements without compromising reliability. Artificio's approach to LLM-powered rules engines addresses these requirements through a sophisticated multi-agent architecture that combines specialized AI components with robust validation and transparency mechanisms.
The foundation of Artificio's rules module lies in its multi-agent validation system. Rather than relying on a single AI model to extract data, interpret rules, and make decisions, the system employs specialized agents that work together to ensure accuracy at each step of the process. Named Entity Recognition (NER) agents focus on identifying and extracting relevant information from documents with high precision. These agents are trained on domain-specific datasets and understand the nuances of different document types, from financial statements to legal contracts to technical specifications.
Once data extraction is complete, reasoning agents take over to interpret the extracted information within the context of applicable business rules. These agents understand relationships between different data points and can evaluate complex conditions that involve multiple factors. For example, when processing a loan application, the reasoning agent doesn't just check individual criteria like credit score and income level, but understands how these factors interact with other considerations like employment stability, debt obligations, and collateral quality.
Validation agents provide a crucial quality control layer by reviewing decisions made by the reasoning agents and checking them against established business logic and historical patterns. This validation process helps catch potential errors before they impact business operations and provides confidence that automated decisions meet the same standards as human-reviewed ones.
Context-aware decision making represents a key differentiator in Artificio's approach. The system understands that the same data might require different interpretations depending on document type, business process, and organizational context. A payment delay mentioned in a vendor invoice requires different handling than the same delay referenced in a customer complaint or internal project report.
This contextual understanding extends to rule interpretation as well. When business rules reference concepts like "reasonable timeframe" or "standard industry practice," the system applies appropriate context based on the specific situation. For construction contracts, reasonable timeframes might be measured in weeks or months, while for software development projects, they might be measured in days or sprints.
The system's ability to maintain context across complex multi-step processes ensures consistency in decision-making even when documents require multiple types of evaluation. For example, a contract might need legal review for compliance issues, financial analysis for budget impact, and operational assessment for resource requirements. The system maintains awareness of insights gained at each step, allowing for more informed final decisions.
Audit trails and transparency mechanisms address the critical need for explainable AI in business operations. Every decision made by Artificio's rules engine includes detailed documentation of the reasoning process, the specific rules applied, and the data points that influenced the outcome. This transparency is essential for regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and continuous improvement of business processes.
The audit trail functionality goes beyond simple logging to provide meaningful insights into decision patterns and system performance. Business users can understand why specific decisions were made, identify areas where rules might need refinement, and track the impact of rule changes over time. This visibility helps organizations build confidence in automated decision-making while maintaining the oversight necessary for critical business processes.
Scalability and flexibility represent fundamental design principles in Artificio's architecture. The system can handle increasing document volumes without compromising accuracy or performance, scaling resources automatically to meet demand. More importantly, the rules engine adapts to changing business requirements without requiring extensive redevelopment or system downtime.
Business users can update rules using natural language descriptions rather than technical specifications, making the system accessible to subject matter experts who understand business requirements but may not have technical backgrounds. When regulations change or business priorities shift, rules can be updated quickly and deployed across the entire system, ensuring consistency in decision-making without lengthy development cycles.
The learning and improvement capabilities built into Artificio's system ensure that accuracy increases over time rather than degrading due to changing business conditions. The system analyzes patterns in decision outcomes, identifies areas where rules might be refined, and suggests improvements based on actual business results. This continuous learning approach helps organizations stay ahead of changing market conditions while maintaining the reliability that critical business processes require.
Integration capabilities ensure that intelligent rules engines can work seamlessly with existing business systems and workflows. Rather than requiring organizations to replace their current infrastructure, Artificio's solution connects with existing ERP systems, document management platforms, and workflow tools, extending their capabilities with intelligent decision-making rather than disrupting established processes.
Measuring Success: ROI and Performance Metrics in Intelligent Automation
Organizations implementing LLM-powered rules engines need clear ways to measure success and demonstrate return on investment. The benefits of intelligent automation extend beyond simple cost savings to include improvements in accuracy, consistency, speed, and strategic capability that can be difficult to quantify but create significant business value.
Processing speed improvements represent the most immediate and measurable benefit of intelligent automation. Documents that previously required hours or days of human review can be processed in minutes, with decisions made according to the same criteria that human reviewers would apply. For high-volume processes like invoice approval or loan processing, these speed improvements translate directly into operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The speed benefits compound when considering the elimination of bottlenecks in business processes. Traditional automation often creates new bottlenecks at the points where human intervention is required, leading to inconsistent processing times and unpredictable workflow completion. Intelligent rules engines eliminate many of these bottlenecks by handling the complex decisions that previously required human review.
Accuracy improvements often prove more valuable than speed gains, particularly in processes where errors create significant downstream costs. Intelligent systems can maintain consistent application of business rules without the fatigue, distraction, or subjective variation that can affect human decision-making. They can also identify patterns and relationships that human reviewers might miss, leading to better outcomes for complex decisions.
Error reduction benefits extend beyond immediate process improvements to include broader business impacts like improved customer relationships, reduced regulatory risks, and better strategic decision-making. When contract reviews are more thorough and consistent, organizations face fewer legal disputes. When loan decisions are more accurate, default rates decrease. When compliance checks are more comprehensive, regulatory risks are minimized.
Cost reduction through automation encompasses both direct labor savings and indirect benefits like reduced error correction, faster time-to-market, and improved resource allocation. While the direct savings from automating manual processes are straightforward to calculate, the indirect benefits often prove more significant over time.
Organizations also see cost benefits from improved decision consistency and quality. Better purchase order approvals lead to improved vendor relationships and pricing. More accurate risk assessments reduce insurance costs and capital requirements. Faster document processing improves cash flow and working capital management.
Scalability advantages become apparent as organizations grow or face increased document volumes. Traditional processes that rely on human review become increasingly expensive and slow as volumes increase, while intelligent automation maintains consistent performance regardless of scale. This scalability enables organizations to pursue growth opportunities that might otherwise be constrained by operational capacity.
Compliance and risk management improvements represent critical but often overlooked benefits of intelligent automation. Consistent application of business rules reduces compliance risks and provides better documentation for regulatory reviews. The audit trail capabilities of intelligent systems create detailed records that support compliance reporting and risk management activities.
The ability to adapt quickly to changing regulations or business requirements provides strategic advantages that are difficult to quantify but create significant competitive value. Organizations can respond to market opportunities, regulatory changes, or competitive pressures more quickly when their operational processes can be updated rapidly and reliably.
Employee satisfaction and strategic focus improvements result from eliminating repetitive, rules-based tasks that often frustrate skilled workers. When employees can focus on strategic analysis, relationship building, and creative problem-solving rather than routine document review, both productivity and job satisfaction increase.
The learning and improvement capabilities of intelligent systems create compounding benefits over time. As systems become more accurate and capable, they can handle increasingly complex decisions, freeing human resources for even higher-value activities. This continuous improvement cycle creates sustainable competitive advantages that traditional automation cannot match.
Looking Forward: The Future of Intelligent Business Process Automation
The evolution of LLM-powered rules engines represents just the beginning of a broader transformation in business process automation. As these systems become more sophisticated and widely adopted, they'll enable new approaches to business operations that go beyond automating existing processes to reimagining how work gets done.
Integration with other AI technologies will create even more powerful automation capabilities. Computer vision integration will enable intelligent processing of visual documents like engineering drawings, site photos, and inspection reports. Natural language generation capabilities will allow systems not just to make decisions but to communicate those decisions in clear, contextually appropriate language that stakeholders can understand and act upon.
Real-time decision making will become possible as processing speeds increase and systems become more tightly integrated with operational processes. Rather than batch processing documents at scheduled intervals, intelligent systems will evaluate transactions, documents, and decisions as they occur, providing immediate feedback and enabling more responsive business operations.
Predictive capabilities will evolve beyond current pattern recognition to enable proactive business management. Systems will identify potential issues before they occur, recommend preventive actions, and optimize resource allocation based on predicted future conditions. This evolution from reactive to proactive automation will create new opportunities for competitive advantage and operational excellence.
The democratization of intelligent automation will make these capabilities accessible to smaller organizations and individual departments within larger enterprises. As the technology becomes more user-friendly and affordable, we'll see intelligent rules engines deployed across a wider range of business functions and organization sizes.
Industry-specific adaptations will create specialized solutions that understand the unique requirements, regulations, and business models of different sectors. Healthcare rules engines will understand medical terminology and regulatory requirements, while manufacturing systems will incorporate supply chain dynamics and quality standards specific to industrial operations.
The integration of intelligent automation with business intelligence and analytics platforms will create comprehensive decision support systems that combine operational automation with strategic insights. Organizations will be able to automate routine decisions while gaining better visibility into business performance and market trends.
Ethical AI and governance frameworks will evolve to address the increasing role of intelligent systems in business decision-making. Organizations will develop sophisticated approaches to ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in automated processes, while regulatory frameworks will provide guidance on appropriate use of AI in different business contexts.
The transformation of work itself will continue as intelligent automation takes over increasingly sophisticated tasks. Rather than replacing human workers, these systems will augment human capabilities, enabling people to focus on creative, strategic, and relationship-based activities that create the most value for organizations and customers.
LLM-powered rules engines represent a fundamental shift from simple task automation to intelligent process optimization. They bridge the gap between data and decisions, enabling organizations to automate not just routine tasks but the complex judgment calls that drive business success. As these systems continue to evolve, they'll create new possibilities for operational excellence, strategic agility, and competitive advantage that will reshape how businesses operate in the digital age.
The organizations that embrace this transformation early and thoughtfully will find themselves with significant advantages in efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability. They'll be better positioned to respond to changing market conditions, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations while freeing their human resources to focus on the strategic and creative challenges that define business success in the 21st century.
