When document processing automation works perfectly, it's invisible. Files flow seamlessly through OCR extraction, data validation, and structured output without anyone noticing. But when exceptions occur, everything grinds to a halt. Suddenly, your streamlined intelligent document processing (IDP) pipeline becomes a bottleneck of manual reviews, escalations, and costly delays.
The reality is that exceptions aren't edge cases anymore. They're a predictable part of any real-world document processing workflow. Whether you're dealing with handwritten notes scribbled in margins, scanned documents that look like they went through a blender, or forms that someone creatively filled out in ways your system never anticipated, these scenarios happen every day. The question isn't whether you'll encounter exceptions, but how efficiently you'll handle them when they inevitably appear.
Most organizations approach exception handling as an afterthought, treating it like a necessary evil that requires throwing more human reviewers at the problem. This reactive approach is expensive, slow, and doesn't scale. What's needed is a proactive strategy that intelligently combines AI automation with human expertise, creating hybrid workflows that learn from exceptions rather than just processing them.
The key insight is that exceptions aren't failures of your IDP system. They're opportunities to make it smarter. When you build robust exception handling into your document processing workflow from the ground up, you create a system that becomes more accurate over time while reducing the manual workload on your team.
The Hidden Cost of Exceptions in IDP Workflows
Before diving into solutions, let's talk about what exceptions are actually costing your organization. The obvious costs are easy to spot: additional staff time for manual review, delayed processing that affects downstream operations, and the administrative overhead of managing exception queues. But the hidden costs often dwarf these visible expenses.
Consider what happens when your document extraction fails on a batch of invoices. First, someone needs to identify which documents didn't process correctly. Then they need to route these documents to the right reviewer, who must manually extract the data while trying to maintain consistency with your automated processing standards. If the reviewer makes a mistake or interprets something differently than your AI would have, you've introduced inconsistency into your dataset that could affect future model performance.
The ripple effects continue downstream. Your accounts payable team is waiting for those invoice details. Your inventory management system needs that supplier information. Your financial reporting depends on accurate, timely data entry. When exceptions create delays, they don't just slow down one process, they impact entire business operations.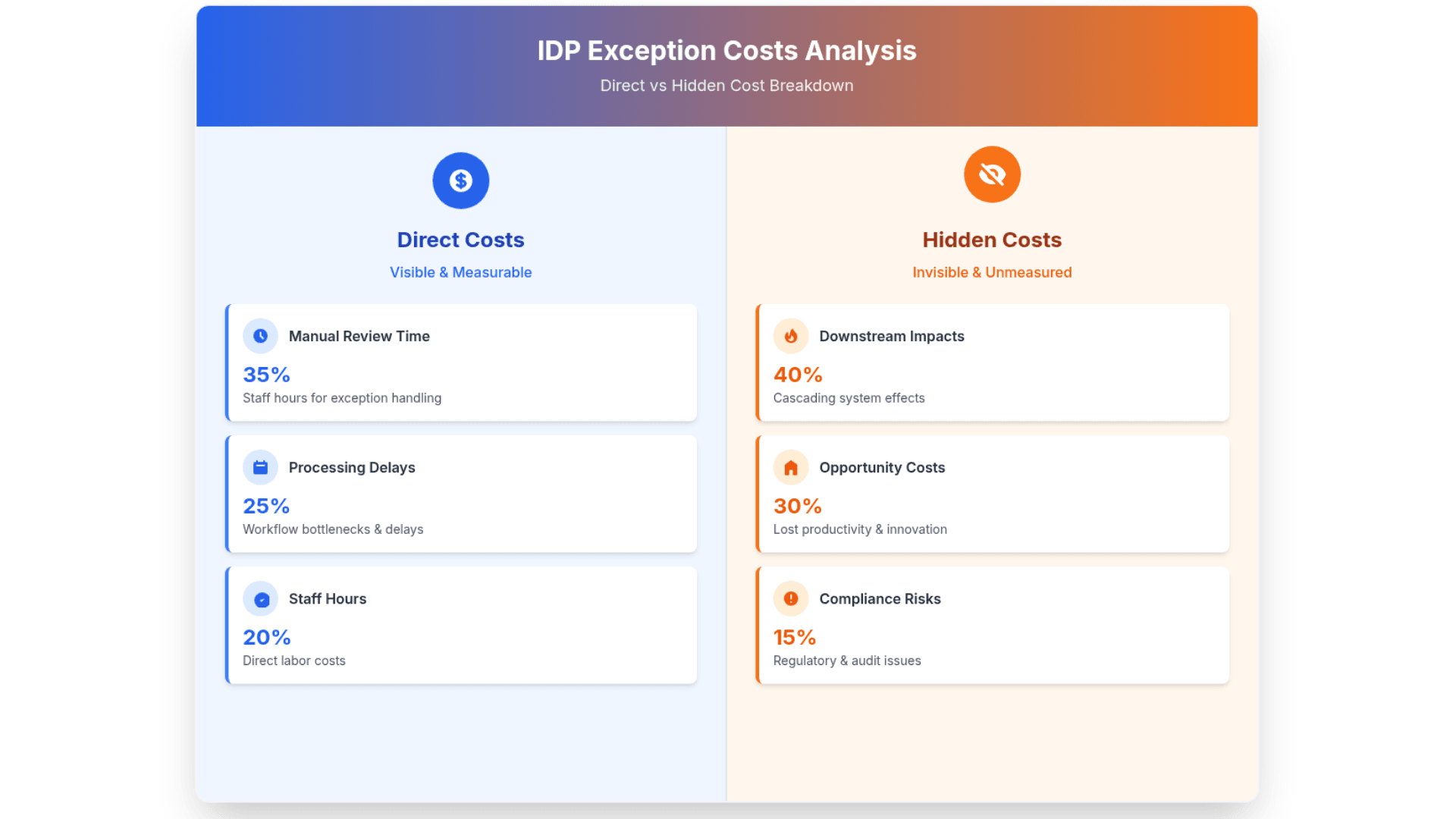
Research from organizations implementing large-scale document processing shows that exception handling can account for 30-50% of total processing costs, even when exceptions represent only 5-15% of total document volume. This disproportionate cost impact happens because exceptions require the most expensive resource in your workflow: human attention and expertise.
The financial impact becomes even more significant when you consider opportunity costs. Every hour your team spends manually processing exceptions is an hour they can't spend on higher-value activities like process improvement, data analysis, or strategic planning. Organizations often find that their most skilled employees become trapped in exception-handling cycles, spending their time on routine data entry rather than the complex problem-solving they were hired to do.
There's also a quality cost that's harder to quantify but equally important. When humans are rushed through exception reviews to meet processing deadlines, error rates increase. These errors compound over time, creating data quality issues that can persist for months or years. Poor data quality affects decision-making, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction in ways that extend far beyond the initial document processing workflow.
Types of Document Exceptions: Understanding What Goes Wrong
Document exceptions come in many forms, but they generally fall into several predictable categories. Understanding these categories helps you design targeted solutions rather than trying to create one-size-fits-all exception handling processes.
Layout variations represent one of the most common exception types. Even when processing documents from the same source, you'll encounter different versions, updated templates, or regional variations that your initial OCR training didn't account for. A supplier might change their invoice format, adding new fields or rearranging existing ones. Government forms get updated with new sections or modified layouts. Even something as simple as a logo change can throw off template-based extraction if your system relies too heavily on visual anchors.
Incomplete forms create another major category of exceptions. Users don't always complete every field, sometimes intentionally and sometimes by accident. They might skip sections they think don't apply to them, leave fields blank because they don't have the information readily available, or simply miss parts of multi-page forms. Your IDP system needs to distinguish between intentionally blank fields and missing data that requires follow-up.
Image quality issues cause frequent exceptions that are often beyond your control. Scanned documents might be tilted, blurry, or have poor contrast. Faxed documents could have artifacts or missing sections. Mobile-captured images might be taken in poor lighting or at awkward angles. While AI has gotten much better at handling imperfect image quality, there are still limits to what automated systems can reliably extract from severely degraded source material.
Handwritten content remains a significant challenge, even with advances in handwriting recognition technology. People have wildly different handwriting styles, they might write outside designated areas, and they often combine print and cursive in unpredictable ways. Medical forms, legal documents, and survey responses frequently contain handwritten annotations that carry important information but require human interpretation.
Data conflicts and inconsistencies represent a more subtle but equally important exception category. This happens when extracted information doesn't match expected patterns or conflicts with other data in the same document. For example, a date field might be interpreted as "13/25/2024" (which is impossible), or calculated totals might not match itemized amounts. These exceptions require not just data extraction but logical validation and error correction.
Unusual document formats and edge cases round out the common exception types. You might encounter multi-column layouts that confuse standard OCR processing, documents with embedded tables or forms, or files that combine multiple document types in a single submission. Foreign language content, specialized terminology, or industry-specific formats can also trigger exceptions if your system wasn't trained on similar examples.
Understanding these exception types helps you build more targeted automation strategies. Rather than treating all exceptions the same way, you can create specialized handling rules that address specific problem patterns while escalating truly ambiguous cases to human reviewers.
Hybrid Human-AI Designs: Building Intelligent Escalation Systems
The most effective approach to exception handling isn't choosing between human reviewers and AI automation. It's creating intelligent hybrid systems that leverage the strengths of both while compensating for their respective weaknesses. AI excels at consistent, rule-based processing and can handle high volumes without fatigue. Humans excel at contextual interpretation, creative problem-solving, and handling truly novel situations.
Confidence thresholds form the foundation of intelligent escalation. Rather than processing every document the same way, your system should evaluate its confidence in each extraction decision and route documents accordingly. High-confidence extractions can flow straight through to your downstream systems. Medium-confidence extractions might trigger additional validation checks or simplified human review. Low-confidence extractions get routed to specialized reviewers who can provide the detailed attention these complex cases require.
The key is setting these thresholds intelligently based on your specific accuracy requirements and cost constraints. A financial services company processing loan applications might set very conservative thresholds because errors are extremely costly. An e-commerce company processing return forms might accept higher risk levels because the cost of occasional errors is lower than the cost of manual review.
Dynamic threshold adjustment makes these systems even more powerful. Instead of using fixed confidence scores, your system should adjust thresholds based on document type, processing volume, and historical accuracy patterns. During peak processing periods, you might temporarily raise thresholds to maintain throughput. For critical document types, you might lower thresholds to ensure maximum accuracy.
Decision escalation workflows need to be designed with human psychology in mind. When reviewers receive exception documents, they need enough context to make informed decisions quickly. This means providing not just the raw extracted data, but also confidence scores, alternative interpretation options, and relevant historical patterns. A good escalation interface shows reviewers what the AI was uncertain about and why, making it easier for humans to focus their attention on the most critical decision points.
Feedback loops close the circle between human decisions and AI improvement. When reviewers correct extraction errors or make interpretation decisions, that information should flow back into your system to improve future processing. This isn't just about retraining models (though that's important), it's about capturing institutional knowledge and decision patterns that can guide future automation. 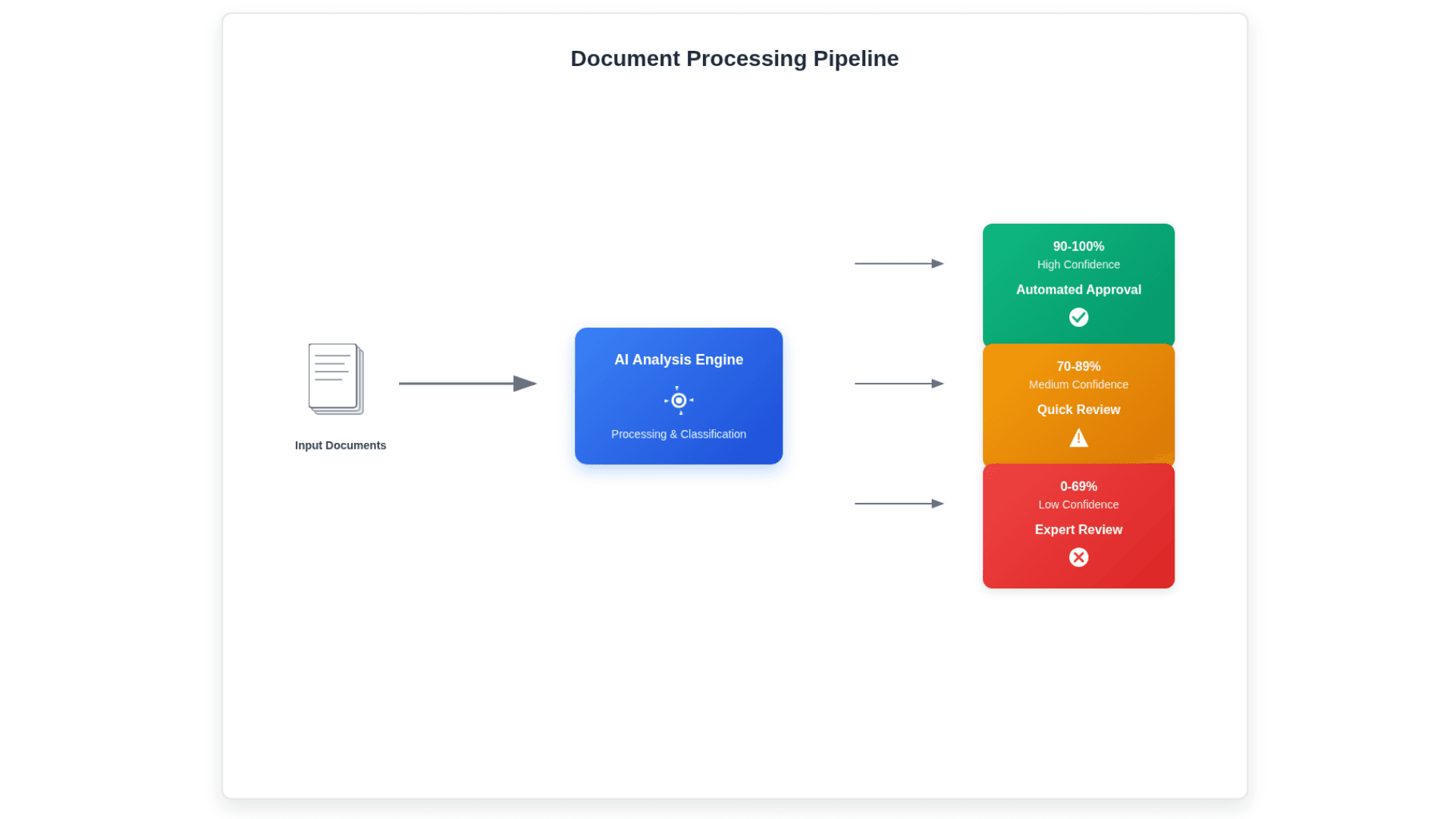
The most sophisticated hybrid systems implement what researchers call "learning-supportive human-in-the-loop" processes. These systems don't just use human input to correct errors, they actively learn from human decision-making patterns to become more autonomous over time. When a human reviewer consistently makes the same type of correction, the system can learn to apply that correction automatically in similar future cases.
This approach requires careful design to avoid creating dependency relationships where humans become bottlenecks rather than force multipliers. The goal is to gradually expand the system's autonomous processing capabilities while maintaining human oversight for genuinely complex or high-stakes decisions.
Smart Validation Agents: Leveraging Artificio's Advanced Tools
Artificio's platform provides several sophisticated tools that can transform exception handling from a reactive process into a proactive, intelligent workflow. The Data Validator and Annotation tools work together to create comprehensive validation pipelines that catch exceptions early and learn from them systematically.
The Data Validator goes beyond simple format checking to implement complex business logic validation. It can verify that extracted dates fall within reasonable ranges, check that calculated totals match itemized amounts, and flag data combinations that don't make business sense. For example, if you're processing insurance claims, the validator might flag cases where the claim amount exceeds the policy limit or where the incident date is after the claim submission date.
More importantly, the Data Validator can be configured to learn from historical patterns. If certain types of inconsistencies frequently turn out to be OCR errors rather than actual data problems, the validator can learn to apply automatic corrections in similar cases. This reduces the number of false positive exceptions while maintaining strict validation for genuinely problematic extractions.
The Annotation workflow tools enable systematic capture of human expertise for complex exceptions. When reviewers encounter ambiguous cases, they can annotate not just their final decision but their reasoning process. This creates a knowledge base of decision patterns that can be used to train more sophisticated validation rules and even guide future AI model development.
These annotation capabilities are particularly powerful for handling regulatory compliance requirements. In industries like healthcare, finance, or legal services, you often need detailed audit trails showing not just what decisions were made but why they were made and who made them. Artificio's annotation tools capture this information automatically as part of the normal exception handling workflow.
The key-pair extractor adds another layer of intelligence by identifying relationships between data elements that might not be obvious from simple field extraction. For example, in processing contracts, it might identify that a signature date should be after the contract effective date, or that certain clauses typically appear together. These relationship patterns can be used to validate extracted data and flag potential exceptions before they reach human reviewers.
Integration between these tools creates powerful synergies. The key-pair extractor can identify relationships that the Data Validator then monitors for consistency. Annotation workflows can capture human corrections that improve both extraction accuracy and validation rules. The entire system becomes more intelligent over time as it learns from the patterns in your specific document types and business processes.
Generative AI Assists: Advanced Exception Resolution Strategies
Recent advances in large language models have opened new possibilities for intelligent exception handling that go far beyond traditional rule-based automation. Generative AI can serve as an intelligent assistant that helps both automated systems and human reviewers handle complex exceptions more effectively.
One powerful application is using LLMs for contextual interpretation of ambiguous content. When OCR extraction produces unclear results, generative AI can analyze the surrounding context to suggest likely interpretations. For example, if a handwritten date is partially illegible, the AI can consider other dates in the document, typical date patterns for that document type, and business logic constraints to suggest the most probable interpretation.
LLM-powered summarization helps human reviewers quickly understand complex exception cases. Instead of presenting reviewers with raw extracted data and error messages, the system can generate plain-English summaries that explain what was extracted successfully, what areas need attention, and what the most likely issues are. This dramatically reduces the cognitive load on human reviewers and helps them make decisions more quickly and accurately.
Generative AI can also assist with data completion and correction. When forms are partially incomplete, LLMs can suggest likely values based on the available information and historical patterns. For business documents, AI can identify when extracted information is internally inconsistent and suggest corrections based on standard business practices and document patterns.
The most sophisticated applications involve using generative AI as a reasoning engine that can explain its decision-making process. When the system encounters an exception, it can generate a detailed explanation of what it attempted to extract, what went wrong, and what additional information would be needed to resolve the issue. This creates a more collaborative relationship between AI systems and human reviewers, where the AI serves as an intelligent assistant rather than just an automated processor. 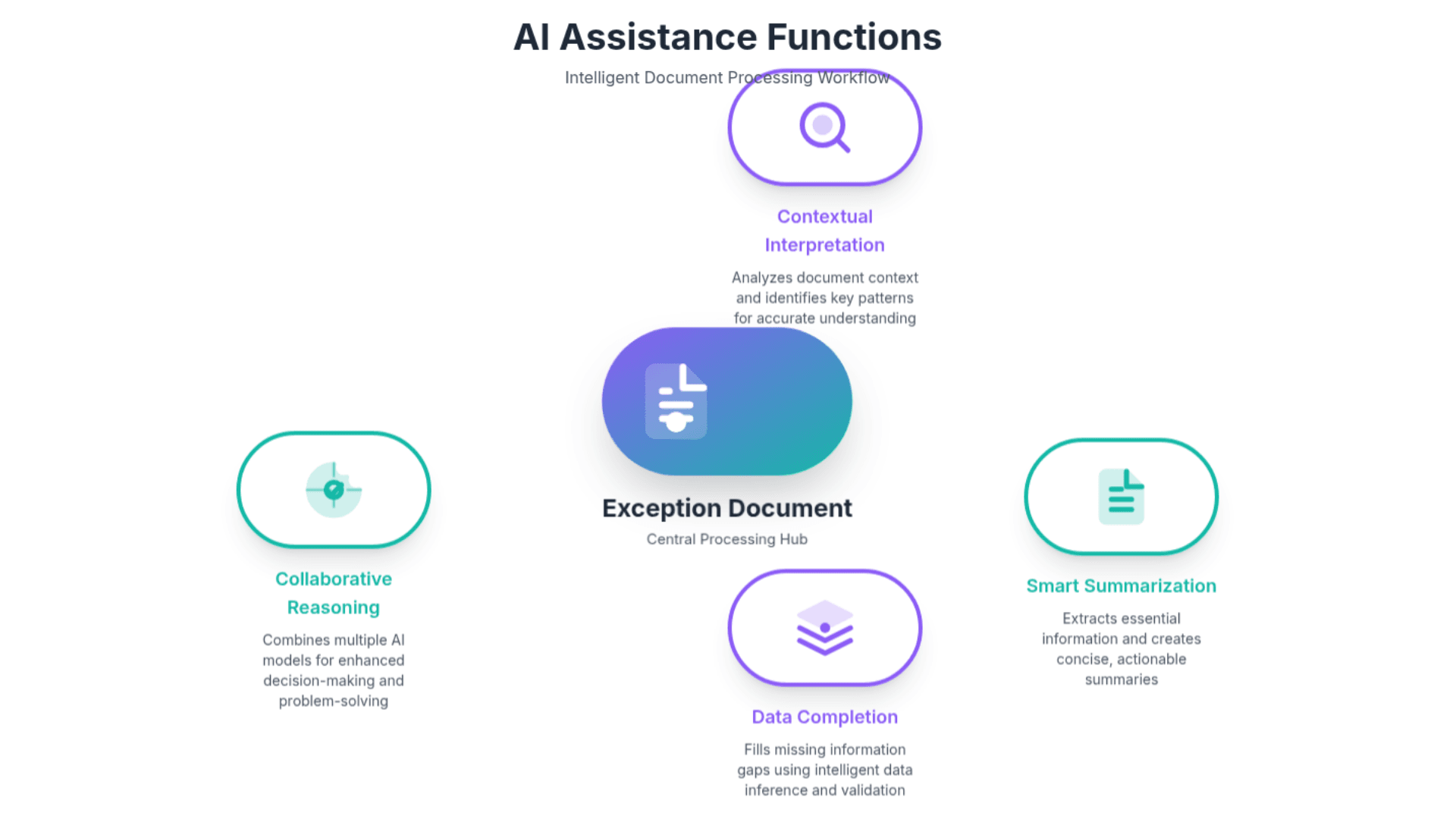
Integration with expense processing workflows, inspired by research like the ERPA system, shows how generative AI can handle domain-specific exceptions intelligently. When processing expense reports, AI can understand business travel patterns, identify unusual expense categories that might need additional review, and even generate explanations for expense approvers about why certain items might be flagged for attention.
The key to successful generative AI integration is maintaining appropriate human oversight while leveraging AI capabilities effectively. AI-generated suggestions should always be clearly marked as such, and human reviewers should have easy ways to accept, modify, or reject AI recommendations. The goal is to augment human decision-making, not replace it.
Workflow Orchestration: Creating Seamless Exception Processing Pipelines
Effective exception handling requires sophisticated workflow orchestration that can route different types of exceptions to appropriate processing paths while maintaining visibility and control over the entire process. Artificio's agent-based architecture provides the flexibility needed to create these complex workflows without sacrificing simplicity or maintainability.
The foundation of good workflow orchestration is intelligent routing based on exception type and characteristics. Different exceptions require different expertise and processing approaches. OCR quality issues might be routed to specialists familiar with image processing techniques. Data validation errors might go to business analysts who understand the underlying business rules. Complex interpretation questions might be escalated to subject matter experts or even external consultants.
Dynamic workload balancing ensures that exception processing doesn't create bottlenecks or overwhelm individual reviewers. The system should monitor processing times, reviewer availability, and exception complexity to distribute work efficiently. During busy periods, simpler exceptions might be batched together for efficient processing, while complex cases get individual attention from experienced reviewers.
Priority management becomes critical when exception volumes are high. Not all exceptions are equally urgent or important. A system processing insurance claims might prioritize exceptions related to high-value claims or time-sensitive regulatory requirements. Invoice processing systems might prioritize exceptions that affect vendor payments or cash flow management.
Progress tracking and visibility help managers understand system performance and identify improvement opportunities. Dashboards should show not just exception volumes and processing times, but also patterns in exception types, reviewer performance, and resolution accuracy. This information guides both operational decisions and long-term system improvements.
Integration with downstream systems ensures that exception resolution doesn't create gaps or inconsistencies in your broader business processes. When exceptions are resolved, the corrected data should flow seamlessly into your ERP systems, databases, or other applications that depend on processed document information. Audit trails should capture the complete history of exception handling for compliance and quality assurance purposes.
Automated retry and recovery mechanisms can handle many exceptions without human intervention. If OCR extraction fails due to image quality issues, the system might automatically apply image enhancement techniques and retry extraction. If data validation fails due to format inconsistencies, automated normalization rules might resolve the issue. These automated recovery attempts should be logged and monitored to identify systemic issues that might require process improvements.
The most sophisticated orchestration systems implement adaptive workflows that adjust their behavior based on performance patterns and feedback. If certain types of exceptions consistently require the same corrections, the system can learn to apply those corrections automatically. If specific reviewers consistently excel at particular exception types, the routing algorithms can learn to leverage their expertise more effectively.
ROI and Accuracy Gains: Measuring Exception Handling Success
Understanding the return on investment from improved exception handling requires looking beyond simple cost savings to consider the broader impact on business operations and data quality. Organizations that implement sophisticated exception handling strategies typically see benefits that compound over time as their systems become more intelligent and efficient.
Direct cost savings come from reduced manual processing time and improved reviewer efficiency. When exceptions are routed intelligently and reviewers have better tools and information, they can process cases more quickly and accurately. Case studies from organizations using advanced exception handling show processing time reductions of 40-60% for complex exception cases, with accuracy improvements of 15-25% compared to purely manual review processes.
Quality improvements often provide even greater long-term value than immediate cost savings. When exception handling processes are designed to learn from human corrections and apply that knowledge systematically, data quality improves across the entire processing pipeline. Better data quality reduces downstream errors, improves decision-making, and reduces the need for data cleanup and correction activities.
Scalability benefits become apparent as processing volumes grow. Traditional exception handling approaches require proportional increases in human reviewers as document volumes increase. Intelligent hybrid approaches can handle much larger volume increases with smaller increases in human resources, because the AI components become more capable over time while human reviewers focus on increasingly complex or novel cases.
Compliance and audit benefits are particularly important in regulated industries. Sophisticated exception handling systems provide detailed audit trails, consistent application of business rules, and clear documentation of decision-making processes. This reduces compliance risk and makes regulatory audits more straightforward and less disruptive.
Risk reduction represents another significant benefit that's often undervalued. When exception handling is ad hoc and inconsistent, there's always risk that important issues will be missed or handled incorrectly. Systematic exception handling with appropriate validation and oversight reduces the risk of costly errors or compliance failures.
Consider a healthcare organization processing medical claims. Before implementing intelligent exception handling, they spent an average of 45 minutes manually reviewing each exception case, with a 12% error rate in manual corrections. After implementing a hybrid system with intelligent routing, automated validation, and learning-supportive workflows, average processing time dropped to 18 minutes per case, with error rates falling to 3%. More importantly, the system began automatically resolving 35% of cases that previously required manual review, creating additional capacity for handling more complex cases.
The financial impact extended beyond direct processing costs. Improved data quality reduced downstream billing errors, faster exception resolution improved cash flow, and better audit trails reduced compliance costs. The total ROI exceeded 300% within the first year, with benefits continuing to grow as the system learned from additional cases.
Best Practices and Implementation Tips
Successfully implementing intelligent exception handling requires careful attention to both technical and organizational factors. Many organizations focus exclusively on the technology components while neglecting the human factors and process changes that are equally critical to success.
Threshold tuning requires ongoing attention and refinement. Initial confidence thresholds should be conservative, erring on the side of sending more cases to human review rather than allowing errors to pass through undetected. As you gather data on system performance and human correction patterns, you can gradually adjust thresholds to optimize the balance between automation and accuracy. This process should be systematic and data-driven, not based on intuition or pressure to reduce manual workload.
User interface design for exception reviewers can make or break the effectiveness of your hybrid workflow. Reviewers need interfaces that present information clearly, highlight areas of uncertainty, and make it easy to provide corrections and feedback. The best interfaces show not just what needs to be reviewed, but why it needs review and what the system's alternative interpretations might be. Context is crucial for efficient human decision-making.
Training and change management deserve significant attention, especially when transitioning from fully manual processes to hybrid automation. Reviewers need to understand how the new system works, what their role is in the process, and how their feedback contributes to system improvement. Resistance to change is natural, but it can be minimized through effective communication, training, and involvement of key stakeholders in system design and implementation.
Feedback loop design determines how effectively your system learns from human corrections. Feedback should be easy to provide, clearly structured, and immediately useful for system improvement. The best systems make feedback provision a natural part of the exception review process rather than an additional burden on reviewers. Consider implementing gamification elements that recognize reviewers who provide particularly valuable feedback for system improvement.
Performance monitoring should track both operational metrics (processing times, throughput, error rates) and learning metrics (automation rates over time, accuracy improvements, feedback quality). Regular review of these metrics helps identify improvement opportunities and ensures that the system continues to evolve in the right direction.
Integration planning needs to consider not just technical integration with existing systems, but also process integration with existing workflows and organizational structures. Exception handling touches many parts of the organization, from IT operations to business users to compliance teams. Successful implementations involve all relevant stakeholders in planning and design processes.
Data governance becomes increasingly important as exception handling systems accumulate knowledge and make autonomous decisions. Clear policies should govern how human feedback is used, how system learning is validated, and how decisions are audited and reviewed. These policies should balance efficiency with accountability and transparency.
Security and privacy considerations require special attention when implementing cloud-based or AI-enhanced exception handling systems. Document processing often involves sensitive or confidential information that requires appropriate protection throughout the exception handling workflow. Ensure that security measures don't impede legitimate exception processing while maintaining appropriate controls over access and data handling.
Building Resilient, Learning-Supportive Exception Management
The future of intelligent document processing lies not in eliminating exceptions, but in handling them so effectively that they become opportunities for continuous improvement rather than operational bottlenecks. Organizations that approach exception handling strategically, with the right combination of AI automation and human expertise, create competitive advantages that compound over time.
The key insight is that exceptions aren't problems to be solved once and forgotten. They're ongoing sources of information about the real-world complexity of your business processes and document workflows. When you build systems that learn from exceptions systematically, you create capabilities that extend far beyond simple document processing into broader process intelligence and optimization.
Artificio's platform provides the tools and flexibility needed to implement these sophisticated approaches without requiring extensive custom development or deep AI expertise. The combination of intelligent agents, configurable validation rules, and learning-supportive workflows creates a foundation for exception handling that can evolve with your business needs and processing requirements.
The most successful organizations don't wait until exception handling becomes a crisis to address it proactively. They build robust exception management into their document processing workflows from the beginning, creating systems that anticipate and handle complexity rather than being overwhelmed by it. This proactive approach pays dividends not just in cost savings and efficiency improvements, but in organizational capability and competitive advantage.
As document processing volumes continue to grow and document types become increasingly diverse, the ability to handle exceptions intelligently will become a key differentiator between organizations that thrive and those that struggle with operational complexity. The time to build these capabilities is now, before exception handling becomes a constraint on your business growth and operational effectiveness.
The investment in intelligent exception handling pays returns not just in immediate operational improvements, but in organizational learning and capability development that creates lasting competitive advantages. When your document processing systems become more intelligent over time, when your human experts can focus on high-value activities rather than routine exception handling, and when your data quality improves continuously through systematic learning, you've created a foundation for sustained business success in an increasingly document-intensive world.
