Introduction
The digital transformation of business processes has entered a pivotal phase where the integration of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology has become instrumental in bridging the gap between physical documentation and digital workflows. This technological advancement represents far more than a simple automation tool; it embodies a fundamental shift in how organizations approach document processing, data management, and information accessibility. The implementation of OCR technology has demonstrated remarkable potential across various industry sectors, offering solutions to long-standing challenges in document processing while enabling new possibilities for process optimization and efficiency enhancement.
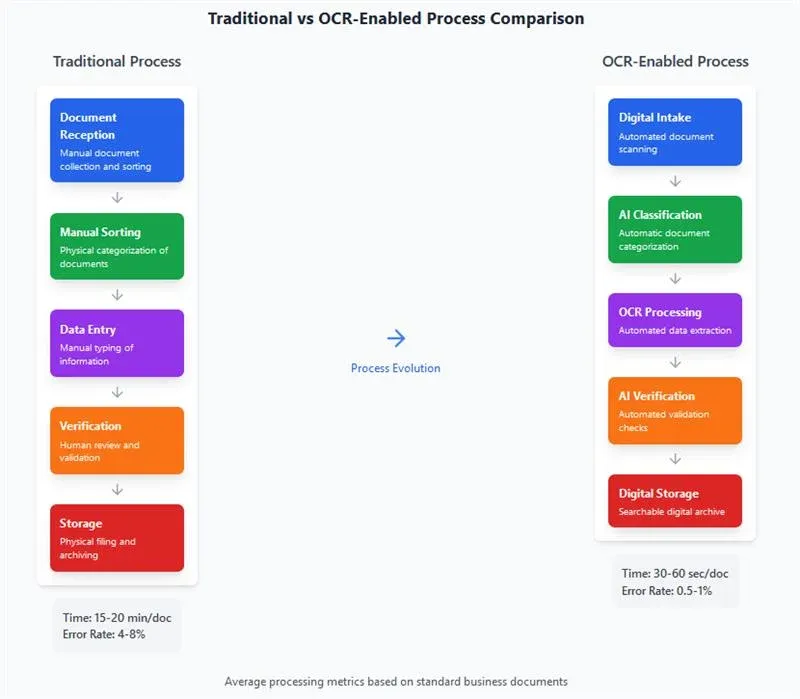
The evolution of OCR technology, particularly its integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, has significantly expanded its applicability and effectiveness in business environments. Modern OCR systems demonstrate sophisticated capabilities in handling diverse document types, multiple languages, and varying document qualities, while maintaining high accuracy levels and processing efficiency. This technological maturity has enabled organizations to implement OCR solutions across various business processes, achieving substantial improvements in operational efficiency while reducing processing costs and error rates.
The selection and implementation of OCR technology require careful consideration of specific use cases and their potential impact on organizational operations. While the technology's applications span numerous domains, certain use cases have emerged as particularly significant in terms of their transformative impact on business processes. These applications demonstrate not only immediate operational benefits but also long-term strategic advantages in terms of scalability, accuracy, and resource optimization. Understanding these key use cases provides organizations with valuable insights into the potential applications and benefits of OCR technology in their specific operational contexts.
The following analysis examines five pivotal applications of OCR technology that have demonstrated remarkable success in streamlining business processes. Each use case is supported by detailed implementation data, performance metrics, and real-world examples that illustrate the transformative impact of OCR technology in specific business contexts. This comprehensive examination aims to provide organizations with actionable insights into the practical applications and benefits of OCR technology across different operational domains.
1. Financial Document Processing and Invoice Management
The processing of financial documents represents one of the most compelling applications of OCR technology, demonstrating remarkable potential for process optimization and cost reduction. In the realm of accounts payable and receivable, traditional manual processing of invoices has long represented a significant operational bottleneck, consuming substantial resources while introducing numerous opportunities for error and delay. The implementation of OCR technology in this domain has revolutionized how organizations handle financial documentation, enabling automated extraction of critical information while maintaining high accuracy levels.
The transformation of invoice processing through OCR implementation encompasses multiple dimensions of operational improvement. Modern OCR systems can automatically extract key data points from invoices, including vendor information, line items, amounts, and payment terms, with accuracy rates exceeding 98% for standardized documents. This automated extraction capability significantly reduces processing time, with organizations reporting reductions from an average of 15 minutes per invoice through manual processing to less than one minute with OCR implementation. The technology's ability to handle various invoice formats and layouts, while maintaining consistent accuracy levels, enables organizations to process higher volumes of financial documents without proportional increases in resource requirements.
Furthermore, the integration of OCR in financial document processing extends beyond simple data extraction to include sophisticated validation and verification capabilities. Advanced OCR systems implement multiple validation layers that automatically verify extracted information against existing records, identify discrepancies, and flag potential issues for review. This automated validation process significantly reduces error rates while enabling more efficient allocation of human resources to exception handling and complex decision-making tasks. The technology's ability to learn from processing patterns and adapt to new document formats ensures continuous improvement in processing accuracy and efficiency.
2. Healthcare Records Management and Patient Documentation
The healthcare sector presents a particularly compelling use case for OCR technology, where the efficient processing of patient records, medical documentation, and insurance claims directly impacts both operational efficiency and quality of care. The transition from paper-based medical records to digital formats has long presented significant challenges for healthcare providers, with traditional manual digitization processes proving both time-consuming and error-prone. The implementation of OCR technology in healthcare environments has enabled more efficient digitization of medical records while maintaining compliance with stringent regulatory requirements.
The application of OCR in healthcare settings encompasses various document types, from patient intake forms and medical histories to laboratory reports and prescription records. Advanced OCR systems demonstrate remarkable capability in processing these diverse document types, achieving accuracy rates above 99% for structured medical forms and maintaining high accuracy levels even for semi-structured documents like clinical notes. The technology's ability to handle medical terminology and specialized notation, while maintaining contextual understanding, enables more accurate extraction of critical medical information.
The impact of OCR implementation in healthcare settings extends beyond immediate operational efficiency gains to include improved patient care outcomes through better information accessibility. Healthcare providers report significant reductions in record retrieval times, from minutes or hours with paper-based systems to near-instantaneous access with digitized records. The technology's ability to make medical records searchable enables more efficient clinical decision support, while automated extraction of key medical information facilitates better coordination of care across different healthcare providers.
3. Legal Document Analysis and Contract Management
The legal sector presents a sophisticated application domain for OCR technology, where the processing of contracts, court documents, and legal correspondence demands both high accuracy and comprehensive understanding of legal terminology. Traditional manual processing of legal documents has historically required significant investment of professional time in document review and analysis. The implementation of OCR technology in legal environments has enabled more efficient processing of legal documentation while maintaining necessary accuracy and compliance requirements.
Modern OCR systems employed in legal applications demonstrate sophisticated capabilities in handling complex legal documents, including multi-page contracts, court filings, and regulatory documentation. The technology's ability to recognize legal terminology, extract key clauses, and identify critical terms enables more efficient contract analysis and review processes. Organizations implementing OCR in legal document processing report reduction in document review times by up to 70%, while maintaining or improving accuracy in key term extraction and classification.
The application of OCR in legal environments extends beyond basic text extraction to include sophisticated analysis capabilities that support legal research and compliance monitoring. Advanced systems can automatically identify and categorize legal citations, track changes across document versions, and flag potential compliance issues for review. This automated analysis capability enables legal professionals to focus on high-value analytical tasks while reducing time spent on routine document review and comparison activities.
4. Government and Public Sector Document Processing
The public sector represents a significant domain for OCR implementation, where the processing of citizen documents, regulatory filings, and administrative records presents unique challenges in terms of volume and complexity. Government agencies at various levels have historically struggled with efficient processing of large document volumes while maintaining necessary accuracy and security requirements. The implementation of OCR technology in public sector environments has enabled more efficient processing of government documentation while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and security standards.
The application of OCR in government settings encompasses various document types, from citizen identification documents and tax returns to regulatory filings and public records. Advanced OCR systems demonstrate remarkable capability in processing these diverse document types, achieving high accuracy rates while maintaining necessary security protocols. The technology's ability to handle multiple languages and document formats enables more efficient processing of citizen documentation in diverse populations.
5. Supply Chain and Logistics Documentation
The logistics and supply chain sector presents a compelling use case for OCR technology, where the efficient processing of shipping documents, customs declarations, and inventory records directly impacts operational efficiency and customer service levels. Traditional manual processing of logistics documentation has historically represented a significant bottleneck in supply chain operations. The implementation of OCR technology in logistics environments has enabled more efficient processing of shipping documentation while improving tracking and visibility capabilities.
Modern OCR systems employed in logistics applications demonstrate sophisticated capabilities in handling various shipping documents, including bills of lading, customs declarations, and delivery receipts. The technology's ability to automatically extract and validate shipping information enables more efficient processing of logistics documentation while reducing errors in data entry and transcription. Organizations implementing OCR in logistics document processing report significant improvements in processing efficiency and accuracy, with some achieving reductions in processing time of up to 80% compared to manual methods.
Conclusion
The examination of these five pivotal use cases demonstrates the transformative potential of OCR technology in modern business environments. Each application domain presents unique challenges and requirements, yet the consistent thread across all implementations is the significant improvement in processing efficiency, accuracy, and resource utilization. The success of OCR implementation across these diverse domains underscores the technology's versatility and adaptability to different operational contexts.
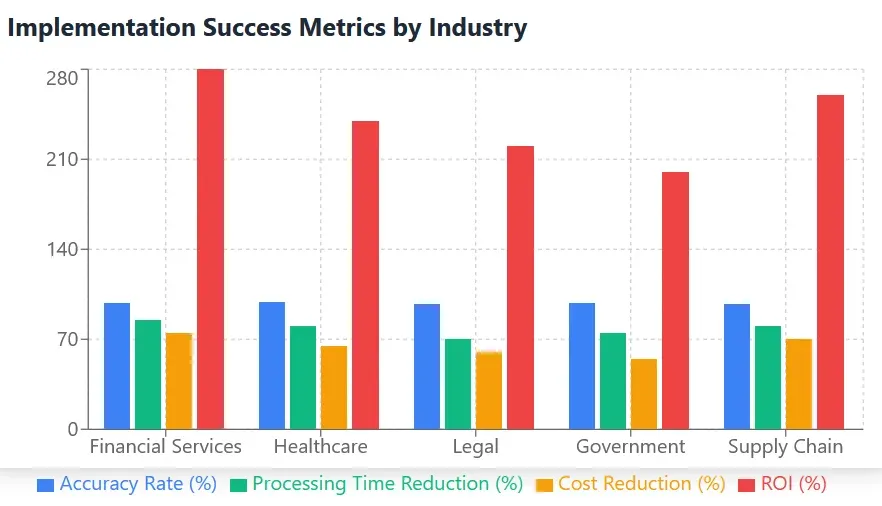
The financial impact of OCR implementation across these use cases demonstrates compelling return on investment, with organizations reporting significant reductions in processing costs while achieving improved accuracy rates.
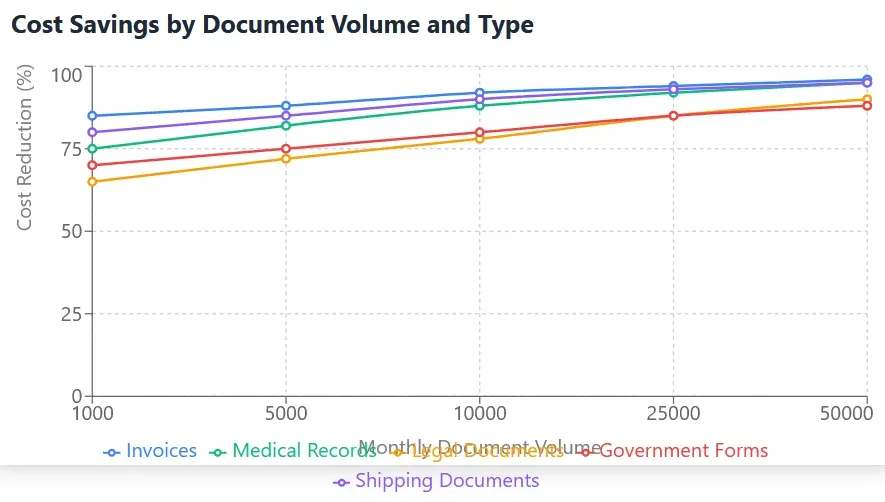
The automation of document processing tasks has enabled organizations to redirect human resources to higher-value activities, improving overall operational efficiency while enhancing employee satisfaction and engagement. The technology's ability to handle increasing document volumes without proportional increases in resource requirements provides organizations with valuable scalability advantages.
The technical evolution of OCR technology, particularly its integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, suggests continued enhancement of capabilities across these use cases. Future developments in areas such as natural language processing, context understanding, and automated learning will likely expand the technology's applications while improving its effectiveness in existing implementations. Organizations that successfully implement OCR technology in these key areas position themselves advantageously for future technological advancements and process optimizations.
The implementation considerations and success factors identified across these use cases provide valuable guidance for organizations planning OCR deployments. The importance of proper system configuration, integration planning, and change management emerges as consistent themes across successful implementations. Organizations must approach OCR implementation as a strategic initiative that requires careful consideration of technical requirements, operational impacts, and user adoption factors.
Looking forward, the role of OCR technology in business process optimization will likely continue to expand, driven by both technological advancements and evolving business requirements. The success demonstrated in these key use cases suggests significant potential for additional applications across various business domains. Organizations that effectively leverage OCR technology in these and similar applications will gain significant advantages in operational efficiency, cost reduction, and process optimization.
In conclusion, the examination of these five use cases illustrates the transformative potential of OCR technology in modern business environments. The technology's ability to improve processing efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance accuracy across diverse applications makes it an essential tool for organizations seeking to optimize their document processing operations. As technology continues to evolve and improve, its role in business process optimization will likely expand, offering new opportunities for efficiency enhancement and process transformation.
