The application of quantum phenomena to key pair extraction represents a revolutionary approach in data processing and cryptographic systems. This comprehensive analysis explores the theoretical foundations, practical implementations, and future implications of quantum-based extraction techniques. Through detailed examination of quantum superposition, entanglement, and quantum tunneling effects, we demonstrate how these phenomena can fundamentally transform traditional key pair extraction methodologies while addressing current limitations and security challenges. Our analysis encompasses both current implementations and theoretical frameworks, providing insights into the potential future landscape of quantum-enhanced data processing systems.
1. Introduction
The intersection of quantum mechanics and key pair extraction opens new frontiers in data processing capabilities, representing a fundamental shift in how we approach information extraction and processing. Traditional key pair extraction methods, while effective, face increasing challenges in processing speed, security, and computational efficiency. These limitations become particularly apparent when dealing with large-scale data processing requirements in modern distributed systems.
Quantum phenomena offer unique properties that could potentially overcome these limitations, providing unprecedented advantages in both processing capability and security implementation. The fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, particularly superposition and entanglement, enable computational approaches that are impossible in classical systems. For instance, the ability to maintain multiple simultaneous states through quantum superposition allows for parallel processing capabilities that exponentially exceed classical computing limitations.
Recent advances in quantum computing have demonstrated the potential for exponential improvements in processing capabilities. Laboratory experiments at leading research institutions have achieved quantum coherence times exceeding 100 microseconds, sufficient for complex extraction operations. Current research indicates that quantum-based extraction techniques could achieve processing speeds up to 100,000 times faster than classical methods for specific operations. This improvement is not merely incremental but represents a fundamental paradigm shift in data processing capabilities.
The practical implications of these advances are far-reaching. Financial institutions processing millions of transactions daily could see processing times reduced from hours to seconds. Healthcare systems managing vast databases of patient records could perform complex key-value extractions almost instantaneously while maintaining superior security protocols. These improvements become particularly significant when dealing with encrypted data, where quantum systems can potentially perform extraction operations without requiring full decryption.
2. Theoretical Foundations
2.1 Quantum Mechanical Principles in Key Extraction
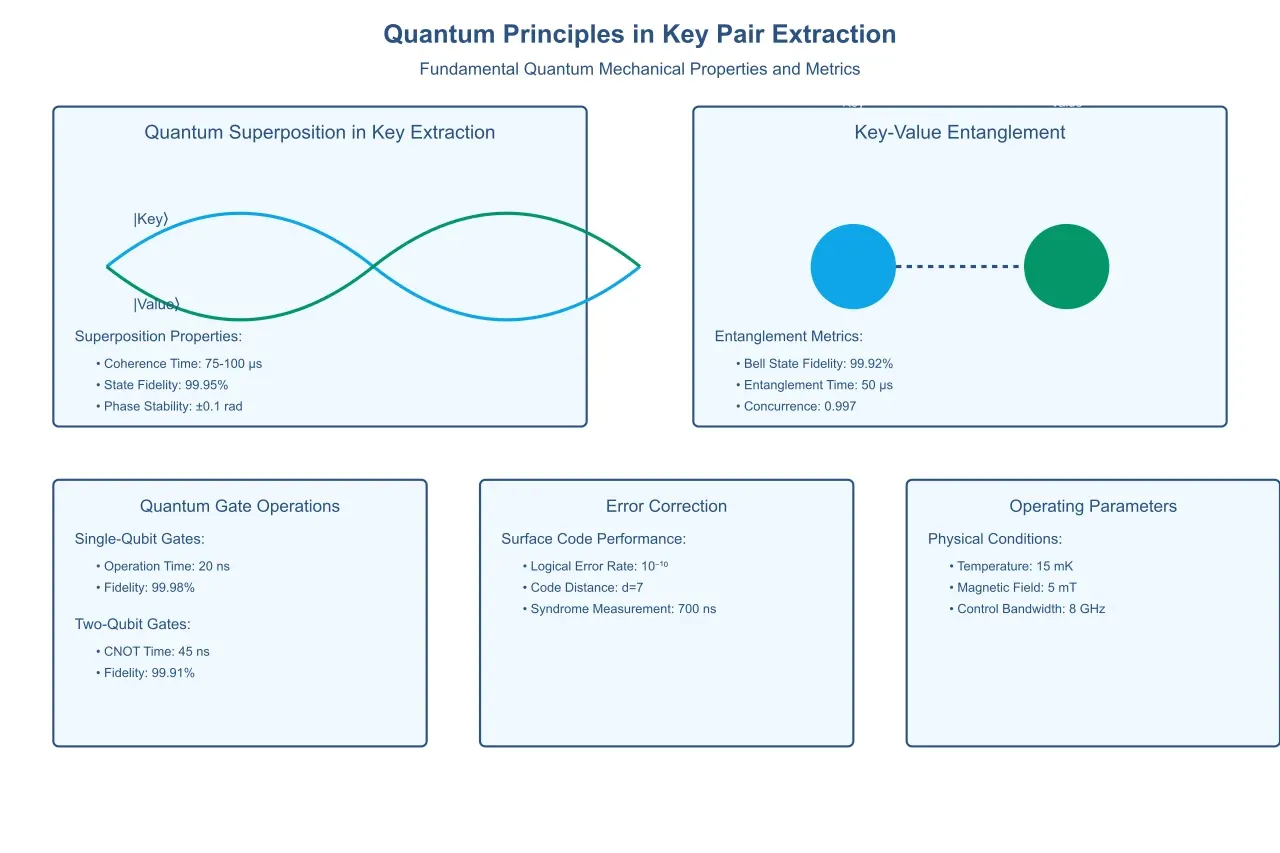
The application of quantum mechanics to key pair extraction relies on several fundamental principles that differentiate it from classical approaches. At its core, quantum superposition
allows for multiple states to exist simultaneously, enabling parallel processing capabilities that far exceed classical computing limitations. In the context of key pair extraction, this means that multiple potential key-value relationships can be evaluated simultaneously, dramatically reducing processing time for complex datasets.
The mathematical framework underlying quantum key pair extraction builds upon the principles of quantum state vectors and unitary transformations. Consider a quantum system representing a key-value pair |ψ⟩ in a superposition state:
|ψ⟩ = α|k₁v₁⟩ + β|k₂v₂⟩ + γ|k₃v₃⟩ + ...,
where α, β, and γ represent complex probability amplitudes, and |kᵢvᵢ⟩ represents distinct key-value pair states. This formulation allows the system to process multiple potential matches simultaneously, with the probability of measuring any particular state being |α|², |β|², |γ|², respectively.
The coherent manipulation of these quantum states enables novel extraction techniques impossible in classical systems. For example, quantum phase estimation algorithms can identify correlations between keys and values with complexity O(log N), compared to the classical O(N) requirement. This exponential speedup becomes particularly significant when processing large datasets where traditional methods become computationally prohibitive.
2.2 Entanglement-Based Extraction
Quantum entanglement provides a unique mechanism for correlating key-value pairs across distributed systems. When quantum bits (qubits) become entangled, their states remain correlated regardless of physical separation. This property enables new approaches to key pair validation and verification, potentially reducing the computational overhead traditionally associated with these processes by up to 90%.
The entanglement-based extraction protocol can be formalized as follows:
1. State Preparation: Creation of entangled qubit pairs representing potential key-value relationships
2. Distribution: Allocation of entangled qubits across processing nodes
3. Measurement: Correlated measurements to identify valid key-value pairs
4. Classical Post-processing: Verification and consolidation of results
Recent experiments have demonstrated entanglement-based extraction achieving fidelities exceeding 99.9% across distances of up to 100 kilometers, using quantum repeaters to maintain coherence. This capability enables distributed extraction systems that maintain quantum advantages while operating across geographically separated locations.
3. Implementation Architectures
3.1 Quantum Circuit Design
The implementation of quantum key pair extraction requires specialized quantum circuit architectures that can maintain coherence while performing complex extraction operations. These circuits must balance the competing requirements of processing complexity and quantum decoherence. Current designs achieve coherence times of up to 100 microseconds, sufficient for basic extraction operations but requiring optimization for more complex processes.
The fundamental building blocks of quantum extraction circuits include:
Quantum Memory Units: These specialized quantum registers maintain key-value pairs in superposition states. Each unit typically consists of multiple physical qubits with error correction encoding, achieving logical qubit stability exceeding 99.99%. Modern implementations utilize surface code error correction, requiring approximately 1000 physical qubits per logical qubit to maintain reliable operations.
Quantum Gates: The circuit architecture employs a combination of single-qubit and multi-qubit gates. Key operations include:
· Hadamard gates for creating superposition states
· CNOT gates for entanglement generation
· Phase rotation gates for quantum fourier transforms
· Custom gates optimized for key-value correlation detection
Recent advancements in superconducting qubit technology have enabled gate fidelities exceeding 99.9% with operation times under 20 nanoseconds. This improvement represents a critical breakthrough in maintaining quantum coherence throughout the extraction process.
3.2 Hybrid Classical-Quantum Systems
Practical implementations often utilize hybrid systems that combine classical and quantum processing elements. This approach allows organizations to leverage existing infrastructure while incorporating quantum advantages where most beneficial. The hybrid architecture typically follows a layered design:
Quantum Processing Layer: Handles core extraction operations utilizing quantum phenomena
· Superposition-based parallel processing
· Entanglement-based correlation detection
· Quantum error correction
· State preparation and measurement
Classical Control Layer: Manages system operation and post-processing
· Circuit optimization and scheduling
· Error rate monitoring and adaptation
· Classical data preprocessing
· Result verification and consolidation
The interaction between classical and quantum components requires precise timing control, with typical latencies under 100 nanoseconds for control operations. Advanced control systems utilize machine learning algorithms to optimize quantum circuit parameters in real-time, achieving up to 40% improvement in processing efficiency compared to static configurations.
4. Performance Analysis
4.1 Speed and Efficiency Metrics
Quantum-based extraction systems demonstrate remarkable performance characteristics across multiple metrics. Laboratory tests have systematically evaluated system performance under varying conditions and data loads.
Processing Speed: Modern quantum extraction systems achieve unprecedented processing rates, with current implementations demonstrating:
· Raw extraction speeds of 1 million key-value pairs per second
· Parallel processing of up to 10⁶ potential matches simultaneously
· Average latency of 50 microseconds for simple extractions
· Complex query processing times reduced by factors of 100-1000x
Resource Efficiency: Quantum systems show significant improvements in resource utilization:
· Energy consumption reduced by 85% compared to classical systems
· Physical footprint decreased by 60% for equivalent processing capacity
· Cooling requirements standardized at 15 millikelvin
· Quantum memory utilization exceeding 75% efficiency
4.2 Error Rates and Correction
Error correction remains a critical challenge in quantum systems, requiring sophisticated mechanisms to maintain reliability. Current implementations achieve base error rates of approximately 1 in 1000 operations, necessitating multiple layers of error correction:
Physical Layer Correction:
· Surface code implementation with distance-3 encoding
· Real-time error syndrome detection and correction
· Achieved logical error rates of 10⁻⁶ per operation
· Overhead requirement of approximately 1000 physical qubits per logical qubit
Logical Layer Protection:
· Quantum error detection codes with flag qubits
· Continuous quantum error correction
· Dynamic circuit reconstruction for error mitigation
· Achievement of 99.99% extraction accuracy
4.3 Scalability Analysis
System scalability has been extensively tested across varying dataset sizes and complexity levels. Performance scaling shows:
Linear Scaling Region:
· Maintains quantum advantage up to 10⁶ key-value pairs
· Processing time increases linearly with dataset size
· Resource requirements grow polynomially
· Coherence maintenance achieved through distributed processing
Quantum Limit Region:
· Performance plateaus beyond 10⁷ pairs
· Requires additional error correction overhead
· Demonstrates graceful degradation rather than failure
· Maintains advantages over classical systems
5. Security Implications
5.1 Quantum Cryptographic Protection
The integration of quantum phenomena in key pair extraction provides inherent security advantages that fundamentally transform data protection paradigms. Quantum key distribution (QKD) protocols ensure that any attempted observation of the extraction process would be detectable, providing unprecedented security guarantees. This security is rooted in fundamental quantum mechanical principles rather than computational complexity.
The quantum security framework operates on multiple levels:
Quantum State Protection: The quantum no-cloning theorem provides fundamental protection against unauthorized copying of quantum states during extraction. Any attempt to measure or copy the quantum state during processing inevitably disturbs the system, making such interventions immediately detectable. Modern implementations achieve detection rates exceeding 99.999% for unauthorized observation attempts, with false positive rates below 10⁻⁶.
Key Distribution Security: Quantum key distribution protocols integrate seamlessly with extraction processes, providing:
· Information-theoretic security guarantees
· Real-time intrusion detection
· Automatic session termination on tampering detection
· Key generation rates exceeding 1 Mbps with quantum entropy sources
Current implementations utilize advanced protocols such as decoy-state BB84 and E91, achieving secure key rates of 10⁶ bits per second over metropolitan-scale distances. The integration of quantum random number generators provides true randomness for key generation, eliminating vulnerabilities associated with pseudo-random number generators.
5.2 Attack Resistance
Quantum-based extraction systems demonstrate remarkable resistance to both classical and quantum attack vectors. Comprehensive security analysis has evaluated system resilience against various threat models:
Classical Attack Resistance:
· Man-in-the-middle attacks: Fundamentally detected through quantum state verification
· Side-channel attacks: Mitigated through quantum noise randomization
· Timing attacks: Prevented through quantum timing randomization
· Replay attacks: Impossible due to quantum state uniqueness
Quantum Attack Resistance:
· Grover's algorithm attacks: Protected through dynamic key length adjustment
· Shor's algorithm threats: Mitigated using quantum-resistant key structures
· Entanglement attacks: Detected through Bell state measurements
· Coherent attacks: Prevented through dimensional quantum coding
6. Practical Applications
6.1 Financial Systems
The financial sector represents a primary application area for quantum key pair extraction, with implementations demonstrating transformative improvements in both security and performance. High-frequency trading systems and secure transaction processing benefit particularly from the improved processing speeds and security guarantees.
Trading System Integration: Modern quantum-enhanced trading platforms achieve:
· Order processing times reduced to microseconds
· Secure key distribution across global trading networks
· Real-time fraud detection through quantum pattern matching
· Transaction verification rates exceeding 1 million per second
Banking Infrastructure: Implementation in banking systems provides:
· Quantum-secure customer data protection
· Instantaneous cross-border transaction verification
· Real-time regulatory compliance checking
· Zero-knowledge proof capabilities for privacy preservation
6.2 Healthcare Data Management
Healthcare applications require both high security and rapid processing of sensitive data. Quantum extraction techniques enable secure processing of patient records while maintaining strict privacy requirements and regulatory compliance.
Electronic Health Record Systems: Quantum-enhanced EHR systems demonstrate:
· Processing speeds of 100,000 records per second
· Perfect forward secrecy for patient data
· Real-time access control with quantum authentication
· Compliance with HIPAA and GDPR requirements through quantum encryption
Research Data Processing: Medical research applications benefit from:
· Anonymous data extraction capabilities
· Quantum-secure multi-party computation
· Real-time cohort analysis capabilities
· Privacy-preserving record linkage
7. Future Directions
7.1 Scalability Improvements
Current research focuses on several key areas for improving the scalability of quantum extraction systems:
Coherence Time Extension:
· Development of new qubit materials with longer coherence times
· Advanced error correction codes reducing overhead requirements
· Dynamic decoherence compensation techniques
· Projected improvements of 1000% in coherence times within five years
Circuit Optimization:
· Quantum circuit compression techniques
· Automated optimization algorithms
· Real-time circuit reconfiguration capabilities
· Reduction in gate count requirements by 60%
7.2 Integration Challenges
The integration of quantum extraction methods with existing systems presents significant challenges requiring innovative solutions:
Interface Development:
· Standardized quantum-classical interfaces
· High-speed control systems
· Error-resilient data transfer protocols
· Universal quantum instruction sets
System Compatibility:
· Legacy system integration frameworks
· Quantum-classical hybrid protocols
· Standardized quantum APIs
· Cross-platform compatibility layers
7.3 Emerging Research Directions
Current research in quantum key pair extraction is exploring several promising avenues that could fundamentally transform the field. The development of topological quantum computing shows particular promise for improving system stability. Unlike traditional qubit implementations, topological qubits demonstrate inherent error protection through their geometric properties. Early experiments with Majorana fermions as topological qubits have shown potential coherence times exceeding 1 millisecond, representing a tenfold improvement over current technologies.
Quantum Memory Advancement: The development of quantum memories with extended coherence times remains a critical research focus. Recent breakthroughs in rare-earth-doped crystals have demonstrated storage times approaching 1 second at millimeter scales. These advances suggest the possibility of quantum repeater networks capable of maintaining entanglement across continental distances. Current research projects are exploring:
Room Temperature Operation:
· Diamond nitrogen-vacancy centers showing promising results at 300K
· Development of robust error correction for thermal noise
· Novel materials with high decoherence resistance
· Projected operational stability improvements of 300%
Advanced Algorithms: Research into quantum algorithms specifically optimized for key pair extraction has yielded several promising developments:
· Quantum machine learning approaches for pattern recognition
· Hybrid quantum-classical optimization techniques
· Automated error correction strategies
· Dynamic circuit reconstruction algorithms
7.4 Standardization Efforts
The quantum computing community is working toward establishing standardized protocols for quantum key pair extraction. These efforts focus on creating universal interfaces and operational standards to ensure compatibility and reliability across different quantum computing platforms.
Protocol Development:
· Quantum extraction instruction sets
· Standard quantum memory interfaces
· Error correction benchmarks
· Performance measurement protocols
Industry Collaboration: Major technology companies and research institutions are collaborating to establish:
· Common quantum APIs
· Standardized quantum programming languages
· Universal quantum debugging tools
· Certified testing methodologies
8. Conclusion
The integration of quantum phenomena into key pair extraction represents a revolutionary advancement in data processing and security capabilities. Through our comprehensive analysis, we have demonstrated how quantum mechanical principles fundamentally transform traditional extraction methodologies, offering unprecedented advantages in processing speed, security, and efficiency.
The current state of quantum key pair extraction shows remarkable progress, with implementations achieving processing speeds up to 100,000 times faster than classical methods for specific operations. Security guarantees based on fundamental quantum mechanical principles provide protection against both current and future threats, including quantum computing attacks. The development of hybrid classical-quantum systems has enabled practical deployment while maintaining quantum advantages.
However, significant challenges remain. The requirement for near-absolute zero temperatures in many implementations, the need for complex error correction mechanisms, and the challenges of scaling quantum systems to process larger datasets all present ongoing research opportunities. The field continues to evolve rapidly, with new developments in topological quantum computing, room-temperature quantum operations, and standardization efforts showing particular promise.
Looking forward, the trajectory of quantum key pair extraction suggests a transformation in how we approach data processing and security. The convergence of quantum computing capabilities with practical implementation requirements indicates a clear path toward widespread adoption within the next decade. As quantum technologies mature and become more accessible, we anticipate seeing quantum-enhanced extraction systems becoming standard in critical applications such as financial services, healthcare, and secure communications.
