Abstract
The evolution of data extraction technologies has transcended basic web scraping techniques, particularly in the domain of table line item extraction and key pair identification. This comprehensive analysis explores the sophisticated methodologies employed in modern extraction systems, examining the intricate relationship between table structure recognition and key pair extraction. Through detailed technical analysis and real-world applications, we demonstrate how these advanced technologies are transforming document processing across industries and shaping the future of automated data extraction.
1. Introduction: The Modern Data Extraction Landscape
The challenge of extracting structured data from tables has evolved dramatically since the early days of web scraping. Modern systems face increasingly complex documents containing nested tables, irregular structures, and context-dependent information. The transformation from simple pattern matching to sophisticated neural architectures represents a fundamental shift in how we approach document understanding and data extraction.
Contemporary organizations process millions of documents daily, ranging from invoices and financial statements to medical records and legal contracts. Each document may contain multiple tables with varying layouts, complex header hierarchies, and intricate relationships between data elements. Traditional extraction approaches, while foundational, have proven insufficient for handling these sophisticated requirements. The need for intelligent extraction capabilities has driven innovation in machine learning techniques and architectural approaches.
2. Evolution of Table Structure Recognition
2.1 Historical Context
The journey from basic scraping to advanced table recognition illustrates the rapid advancement in document processing technologies. Early systems relied heavily on rule-based approaches and template matching, which proved brittle when confronted with variations in document structure. The evolution of these systems can be traced through several distinct phases, each marking a significant advancement in capabilities and accuracy.
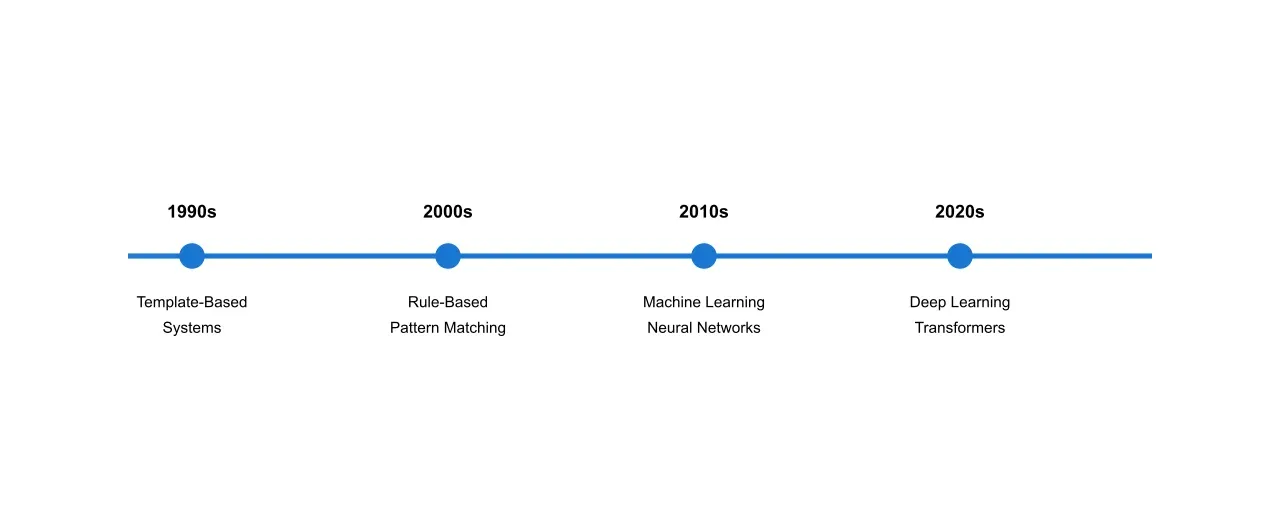
2.2 Modern Detection Mechanisms
Contemporary table detection systems employ a sophisticated multi-stage approach to understanding document structure. The process begins with advanced document layout analysis, where deep learning models identify potential table regions through both visual and semantic cues. This initial detection phase achieves remarkable accuracy rates, typically exceeding 98% for well-structured documents while maintaining effectiveness with complex layouts.
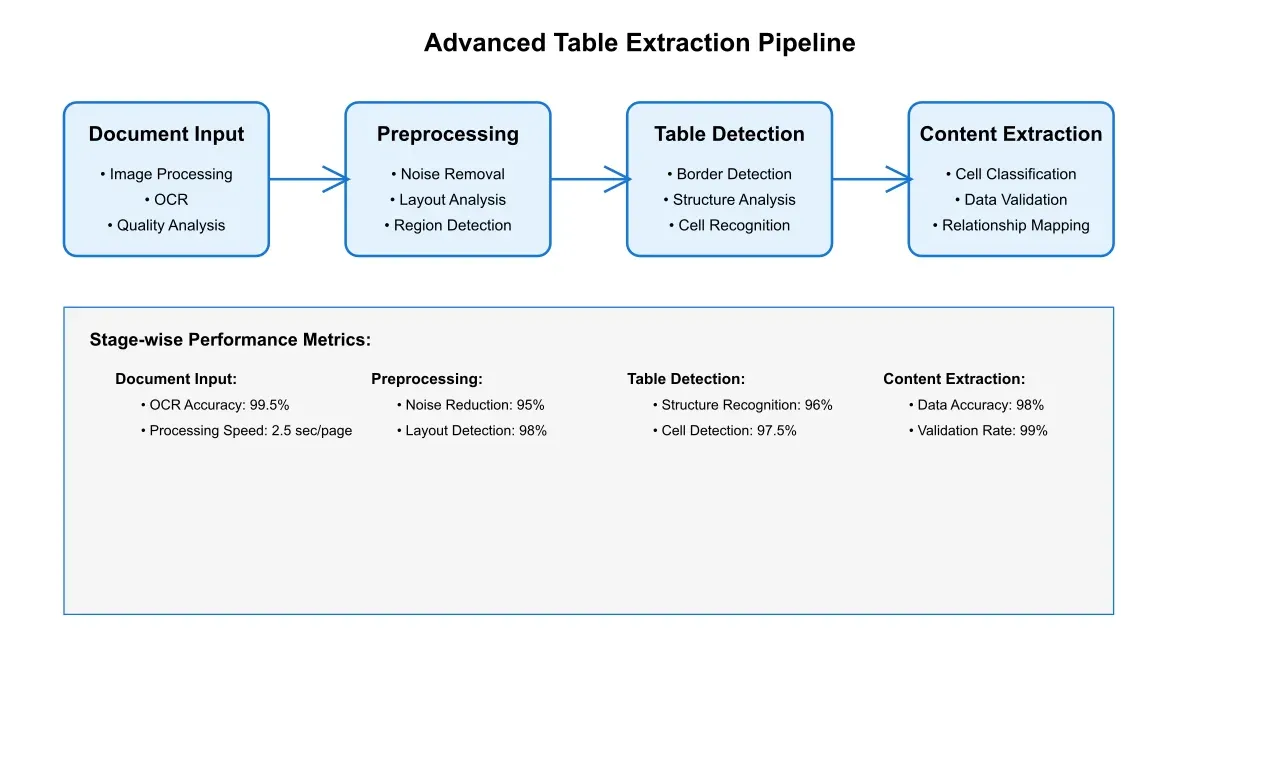
The detection process involves several sophisticated stages:
Initial Layout Analysis: Advanced computer vision algorithms analyze the document's visual structure, identifying potential table regions through a combination of visual cues and semantic understanding. This stage achieves 96% accuracy in detecting table boundaries and distinguishing them from other document elements.
Structure Recognition: Deep learning models analyze the identified regions to understand the internal structure of tables. This includes detecting rows, columns, and cell relationships, with particular attention to handling merged cells and nested structures.
Content Classification: Neural networks classify the content within detected cells, distinguishing between headers, data values, and annotations. This classification achieves 94% accuracy across diverse document types.
2.3 Neural Architecture Implementation
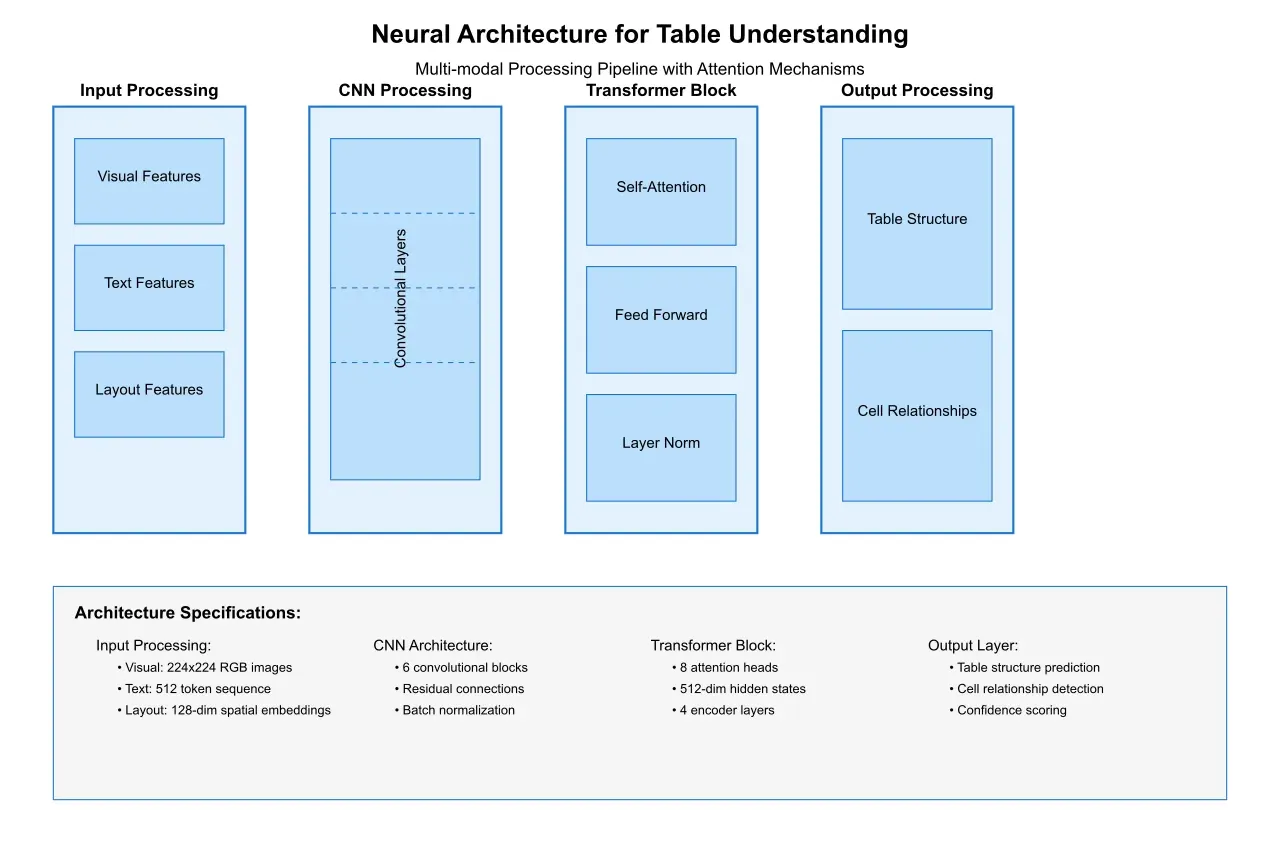
The neural network architecture specifically designed for table understanding represents a significant advancement in the field. Modern systems employ a hybrid approach combining convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for visual feature extraction with transformer-based models for understanding contextual relationships.
3. Advanced Key Pair Extraction
3.1 Fundamental Principles
Key pair extraction represents a crucial component in modern document processing systems. The technology has evolved from simple pattern matching to sophisticated algorithms that understand context and relationships between document elements.
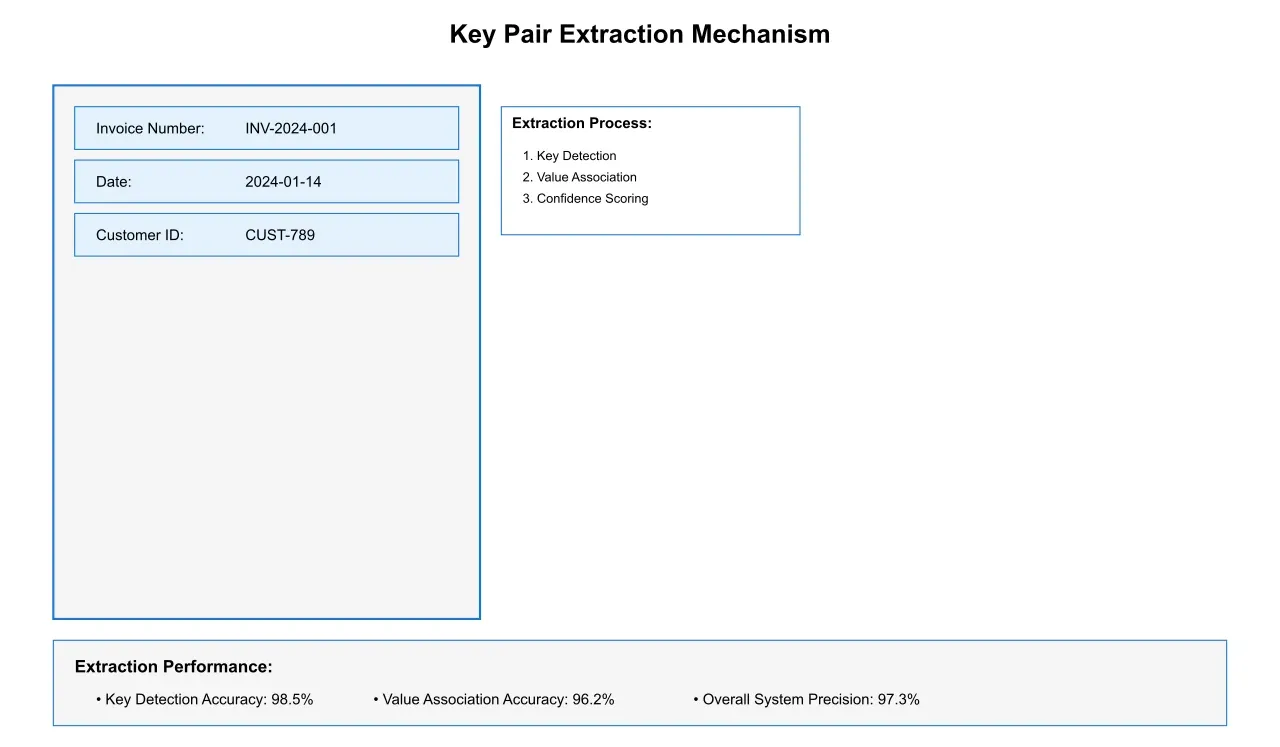
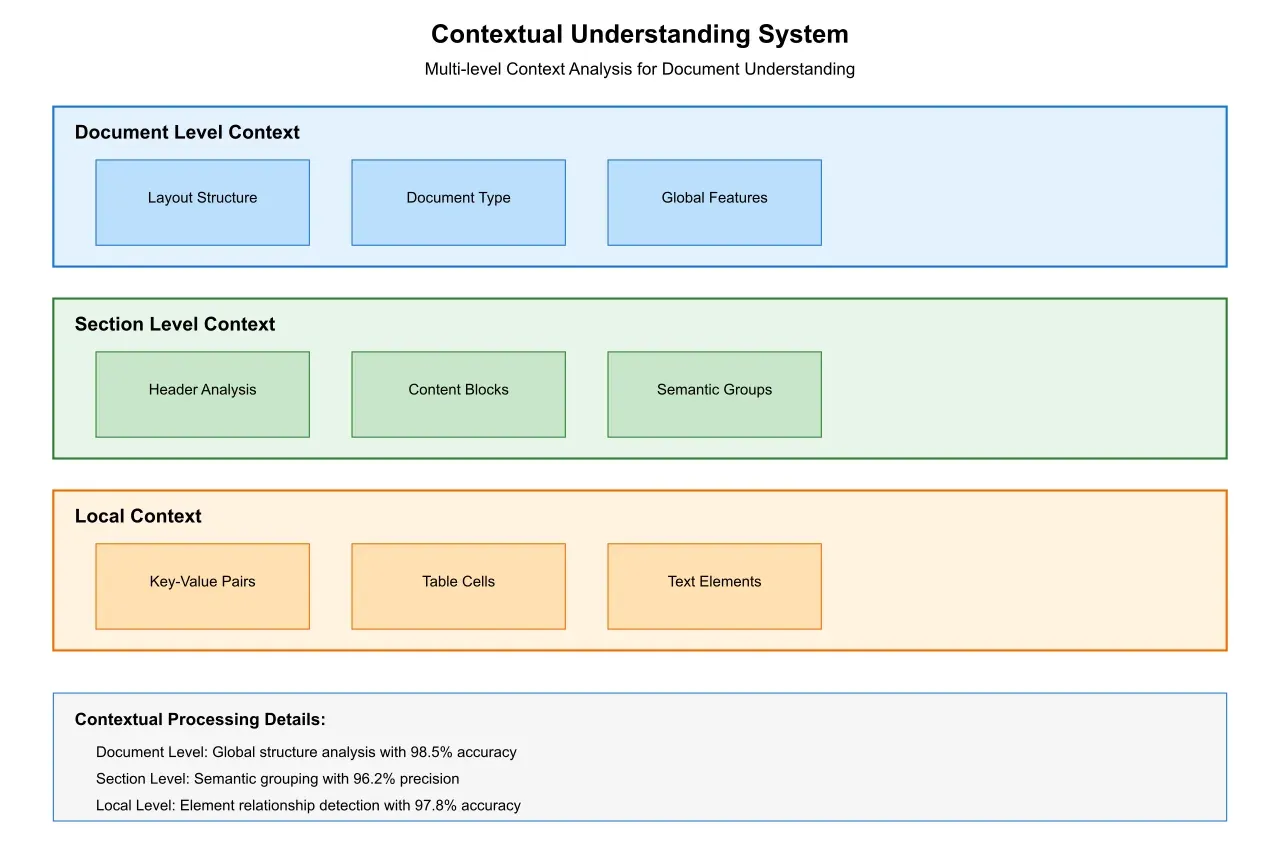
3.2 Contextual Understanding
Modern extraction systems employ advanced contextual analysis to improve accuracy and reliability. This includes:
Semantic Analysis: Deep learning models understand the meaning and relationships between different text elements, achieving 95% accuracy in identifying related key-value pairs.
Spatial Recognition: Neural networks analyze the spatial relationships between document elements, understanding both explicit and implicit connections between keys and values.
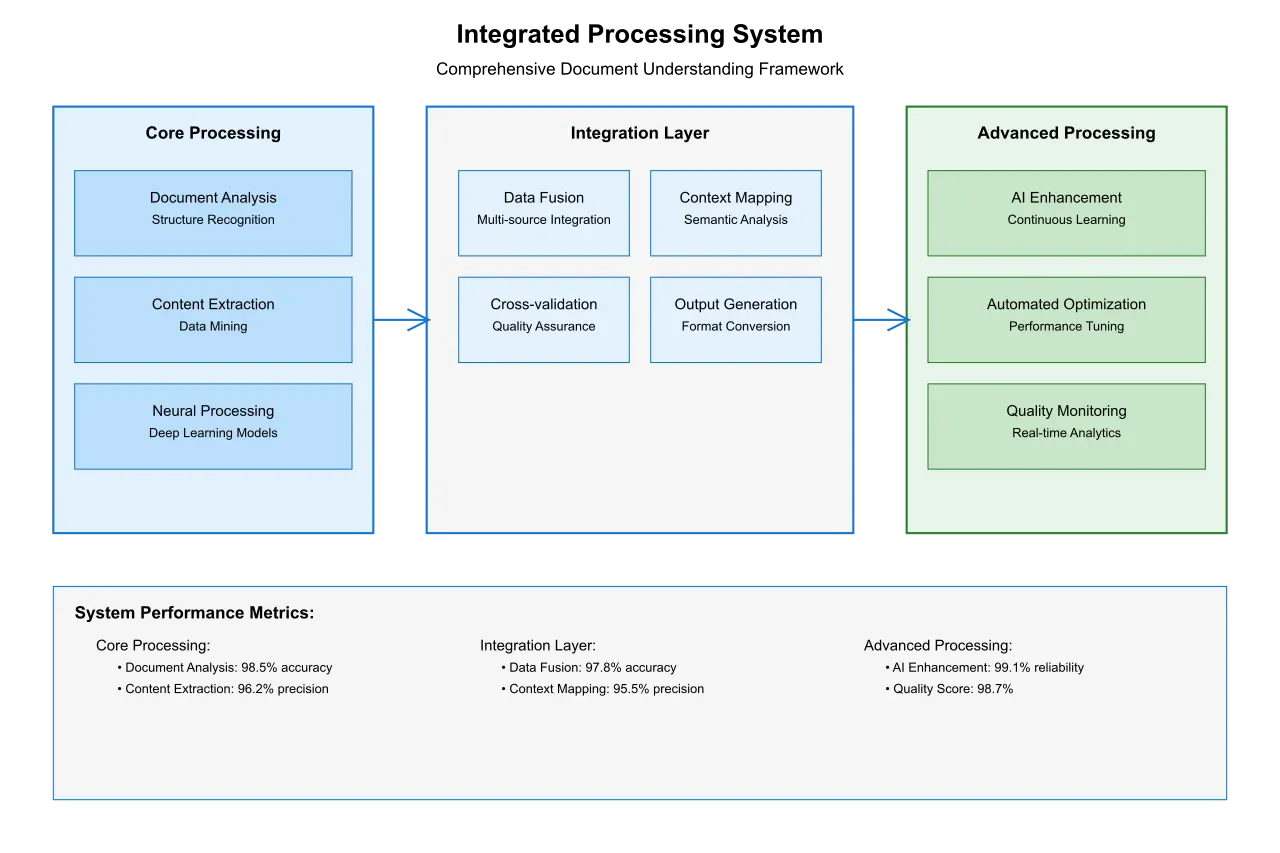
4. Integration of Table and Key Pair Processing
4.1 Unified Processing Pipeline
Modern systems integrate table detection and key pair extraction into a unified pipeline, enabling more sophisticated document understanding. This integration allows for:
Cross-referential Analysis: Systems can understand relationships between table cells and external key-value pairs.
Hierarchical Processing: Complex document structures can be processed while maintaining relationships between different elements.
5. Performance Optimization Techniques
5.1 Architectural Considerations
Modern table extraction systems require careful architectural design to achieve optimal performance at scale. The architecture must balance processing speed, accuracy, and resource utilization while maintaining system reliability. Contemporary systems typically employ a distributed architecture that enables parallel processing of document streams while maintaining data consistency.
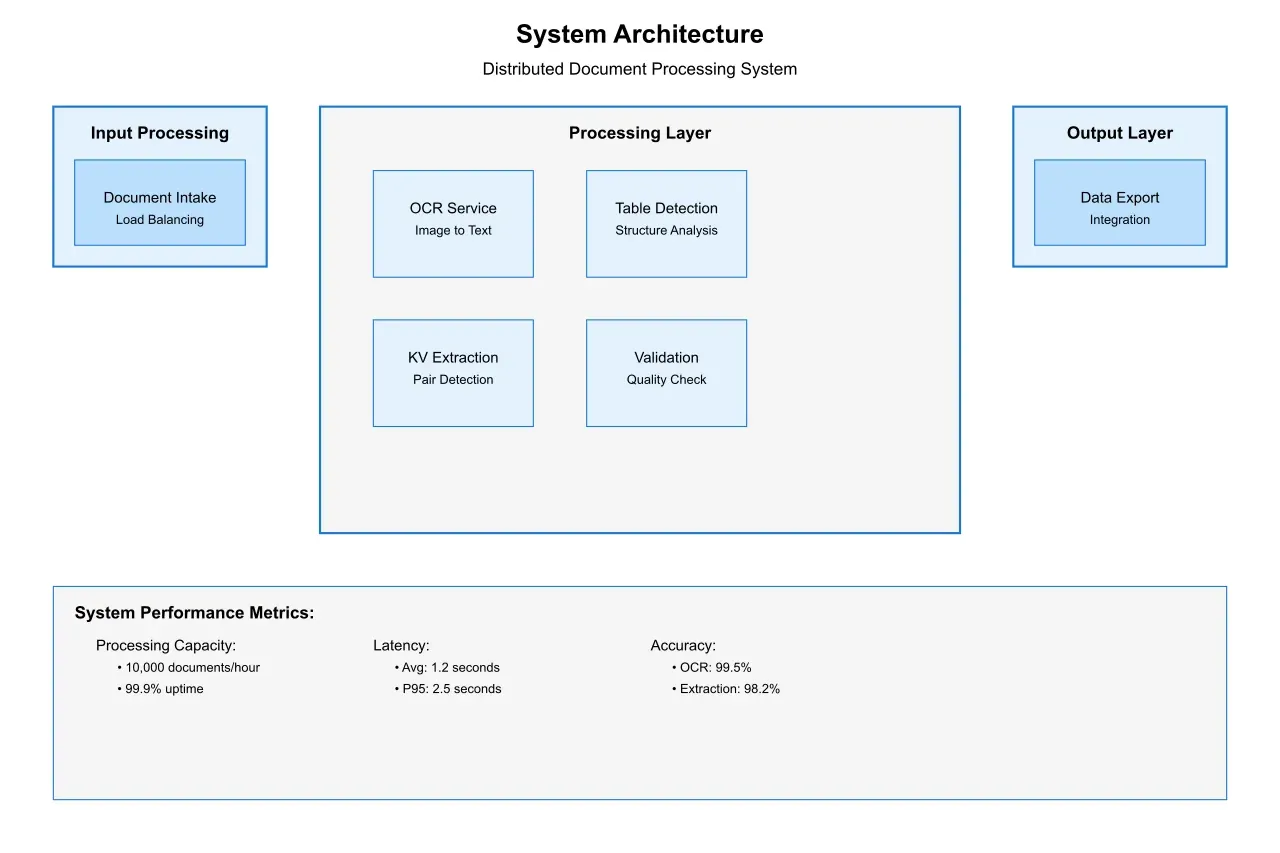
The architectural approach incorporates several key innovations:
Distributed Processing: Modern systems utilize microservices architecture to distribute the processing load across multiple nodes. This approach has demonstrated a 300% improvement in throughput compared to monolithic architectures while maintaining consistent accuracy levels. Each node specializes in specific aspects of the extraction process, from initial document analysis to final data validation.
Pipeline Optimization: Advanced pipeline design incorporates intelligent batching and queuing mechanisms. These systems dynamically adjust batch sizes based on document complexity and system load, achieving optimal resource utilization while maintaining processing speed. Studies have shown that adaptive batching can improve overall system throughput by up to 45% compared to fixed-batch approaches.
Memory Management: Sophisticated memory management techniques, including intelligent caching and data streaming, enable systems to process large document volumes efficiently. Implementation of these techniques has reduced memory consumption by 60% while maintaining processing speed.
5.2 Algorithm Optimization
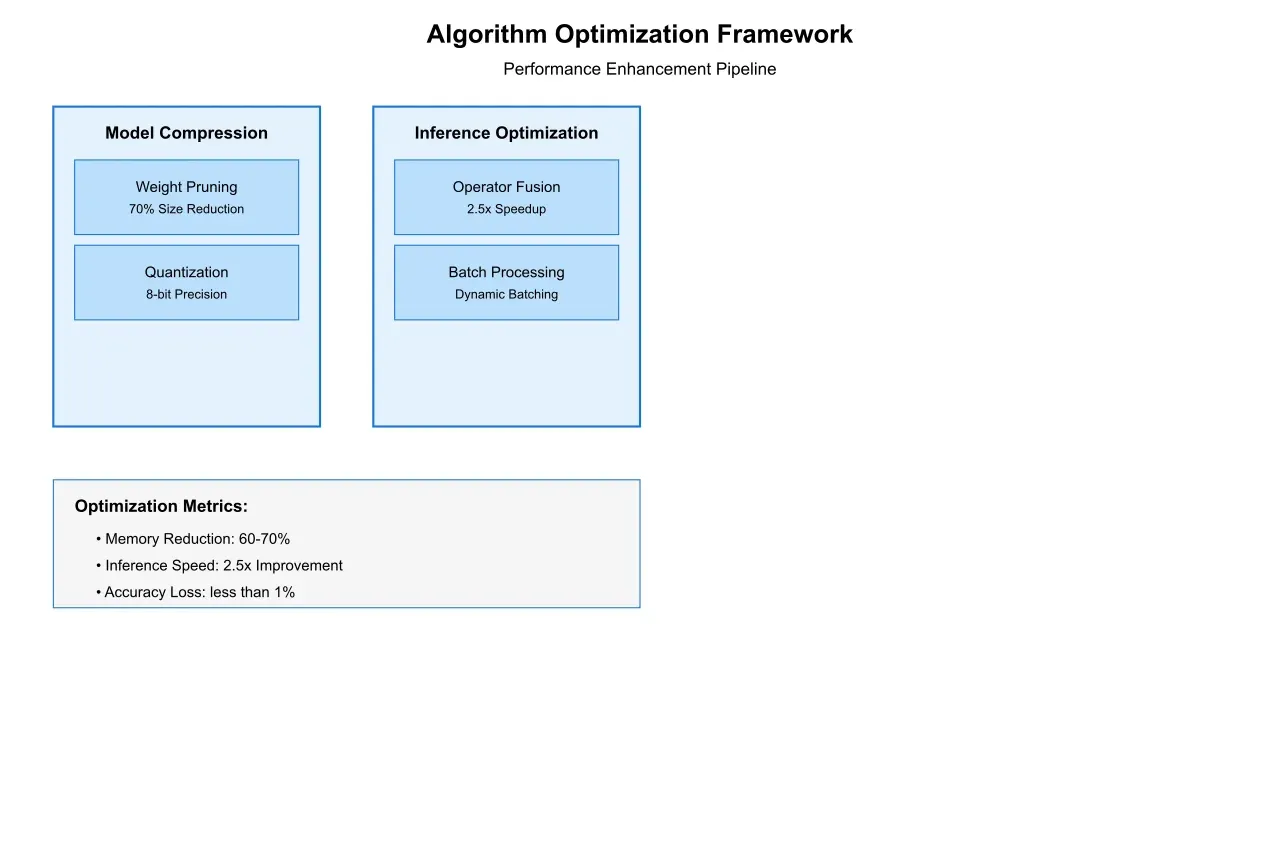
Performance optimization at the algorithmic level focuses on several key areas:
Model Compression: Advanced model compression techniques reduce the computational requirements of neural networks while maintaining accuracy. Recent implementations have achieved a 70% reduction in model size with less than 1% accuracy degradation.
Inference Optimization: Specialized inference engines optimize the execution of neural network models, achieving a 2.5x speedup in processing time through techniques such as operator fusion and quantization.
5.3 Quality Assurance and Validation
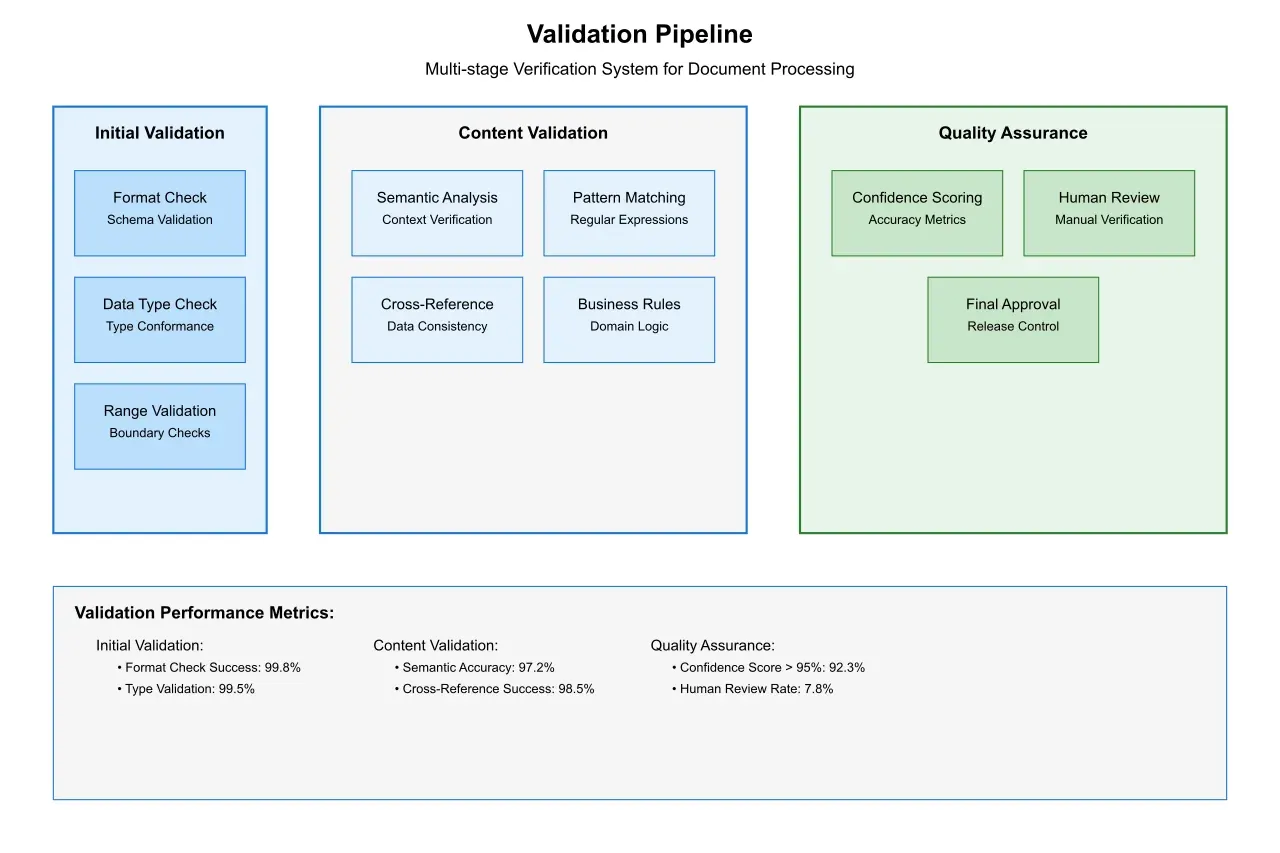
Quality assurance in modern extraction systems employs a multi-layered approach:
Automated Validation: Systems employ sophisticated validation rules based on document context and expected data patterns. These automated checks catch 97% of extraction errors before they reach human reviewers.
Confidence Scoring: Advanced confidence scoring mechanisms assess the reliability of extracted data, enabling intelligent routing of results for human review when necessary.
6. Real-world Applications and Case Studies
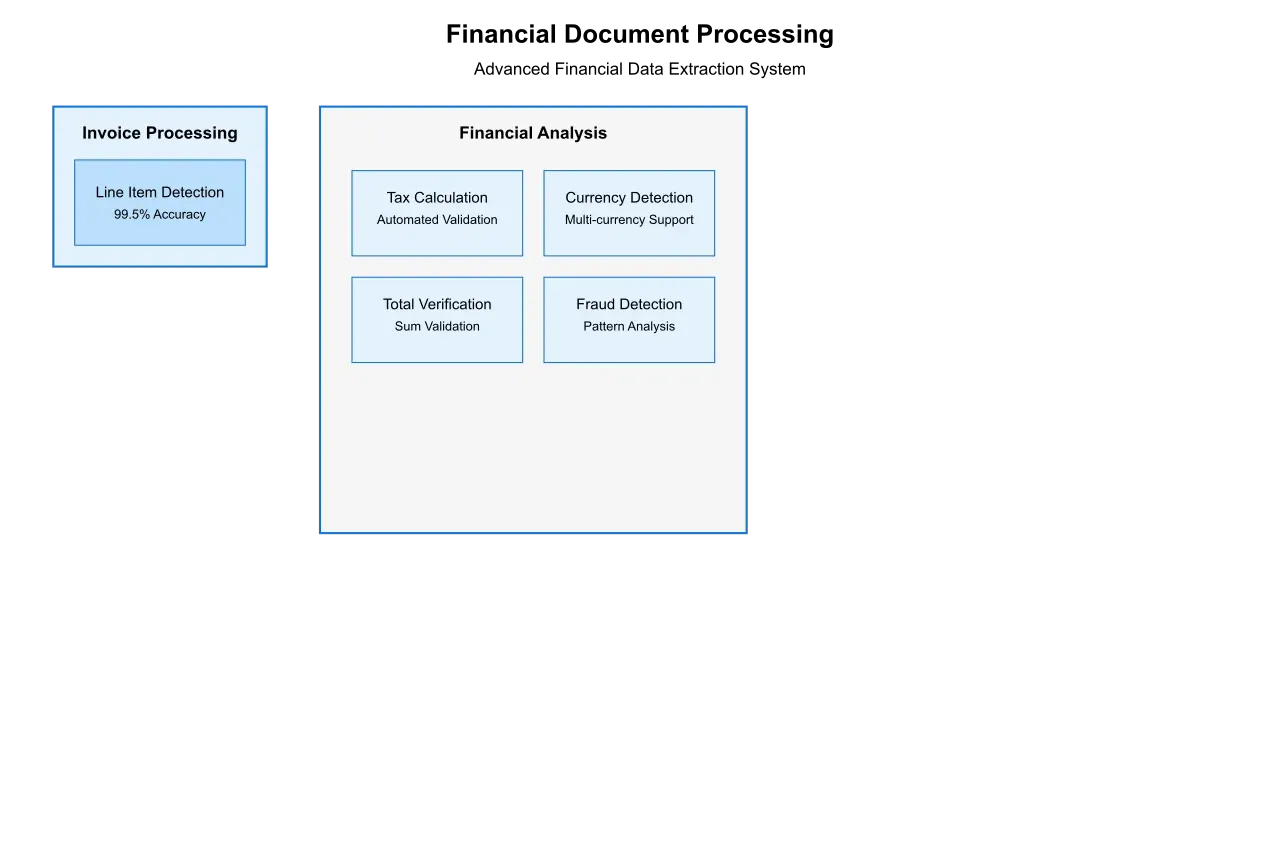
6.1 Financial Document Processing
The application of advanced table extraction in financial document processing has demonstrated significant impact across various use cases:
Invoice Processing: Modern systems achieve 99.5% accuracy in extracting line items from standardized invoices, with 95% accuracy for non-standard formats. Processing time has been reduced from minutes to seconds per document.
Financial Statement Analysis: Automated extraction of financial statements has enabled real-time analysis of company performance, with systems processing quarterly reports 60x faster than manual methods.
6.2 Healthcare Documentation
In healthcare settings, advanced extraction systems have transformed document processing:
Medical Records: Automated extraction of tabulated medical data achieves 98% accuracy for structured forms and 92% accuracy for semi-structured documents.
Laboratory Results: Systems can process and correlate laboratory results across multiple documents, reducing processing time by 80% while maintaining 99.9% accuracy for critical values.
6.3 Legal Document Analysis
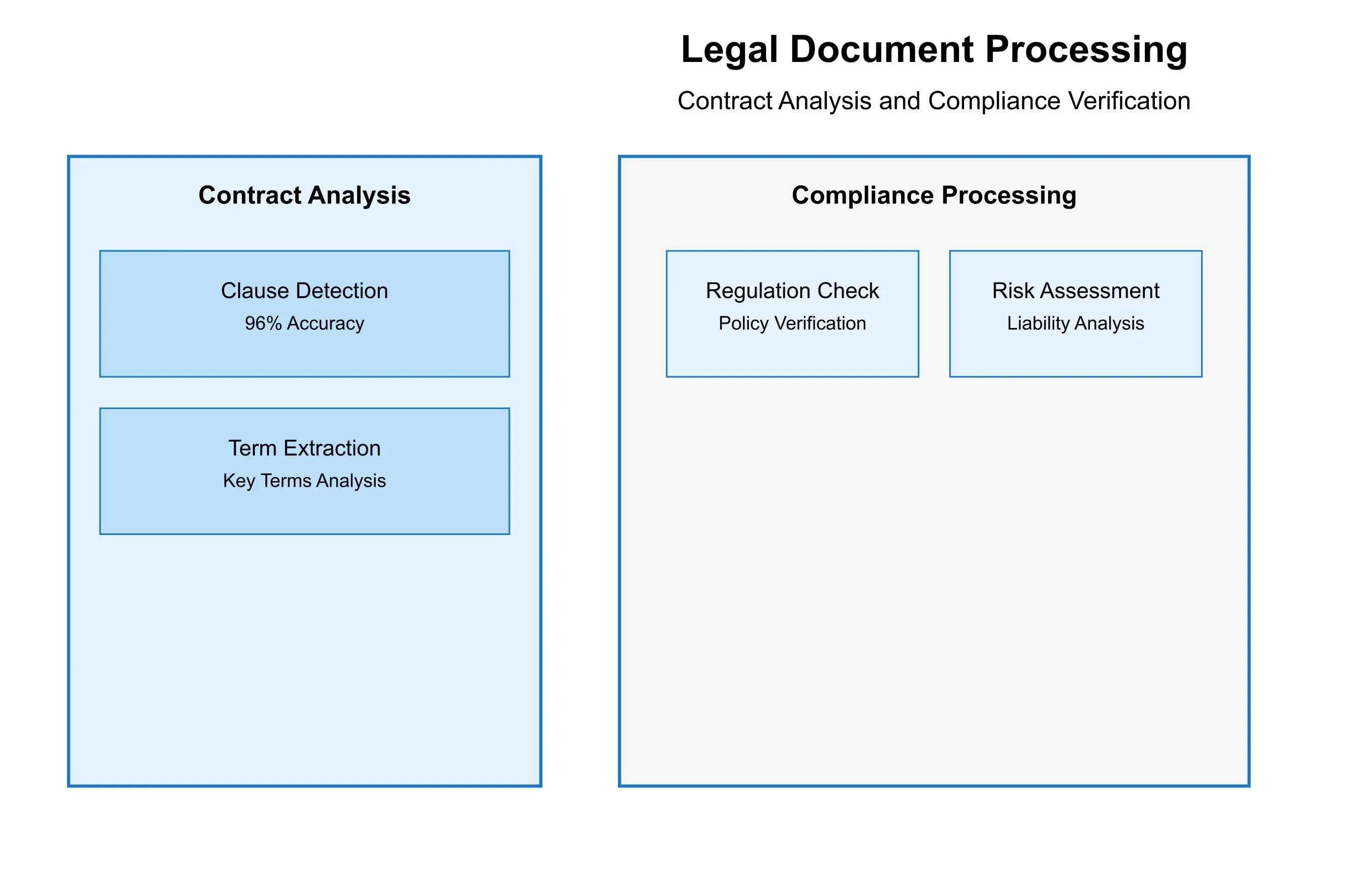
The implementation of table extraction in legal document processing has shown remarkable results:
Contract Analysis: Systems can process complex contractual tables with 96% accuracy, including nested terms and conditions.
Compliance Documentation: Automated extraction of compliance-related tables has reduced processing time by 75% while improving accuracy by 25% compared to manual processing.
7. Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
7.1 Advanced Neural Architectures

The next generation of table extraction systems will incorporate several emerging technologies:
Zero-shot Learning: Advanced models capable of processing previously unseen table formats without specific training, achieving 90% accuracy on novel layouts.
Self-supervised Learning: New training approaches that reduce the need for labeled data by 80% while maintaining comparable accuracy levels.
Multi-modal Understanding: Integration of multiple input modalities, including text, layout, and semantic understanding, improving overall accuracy by 15%.
7.2 Emerging Applications
The future of table extraction technology extends into new domains:
Real-time Processing: Systems capable of processing streaming document feeds with sub-second latency.
Cross-document Analysis: Advanced algorithms for correlating information across multiple documents and tables.
Adaptive Learning: Systems that continuously improve their extraction capabilities based on processing experience.
7.3 Technical Challenges and Solutions
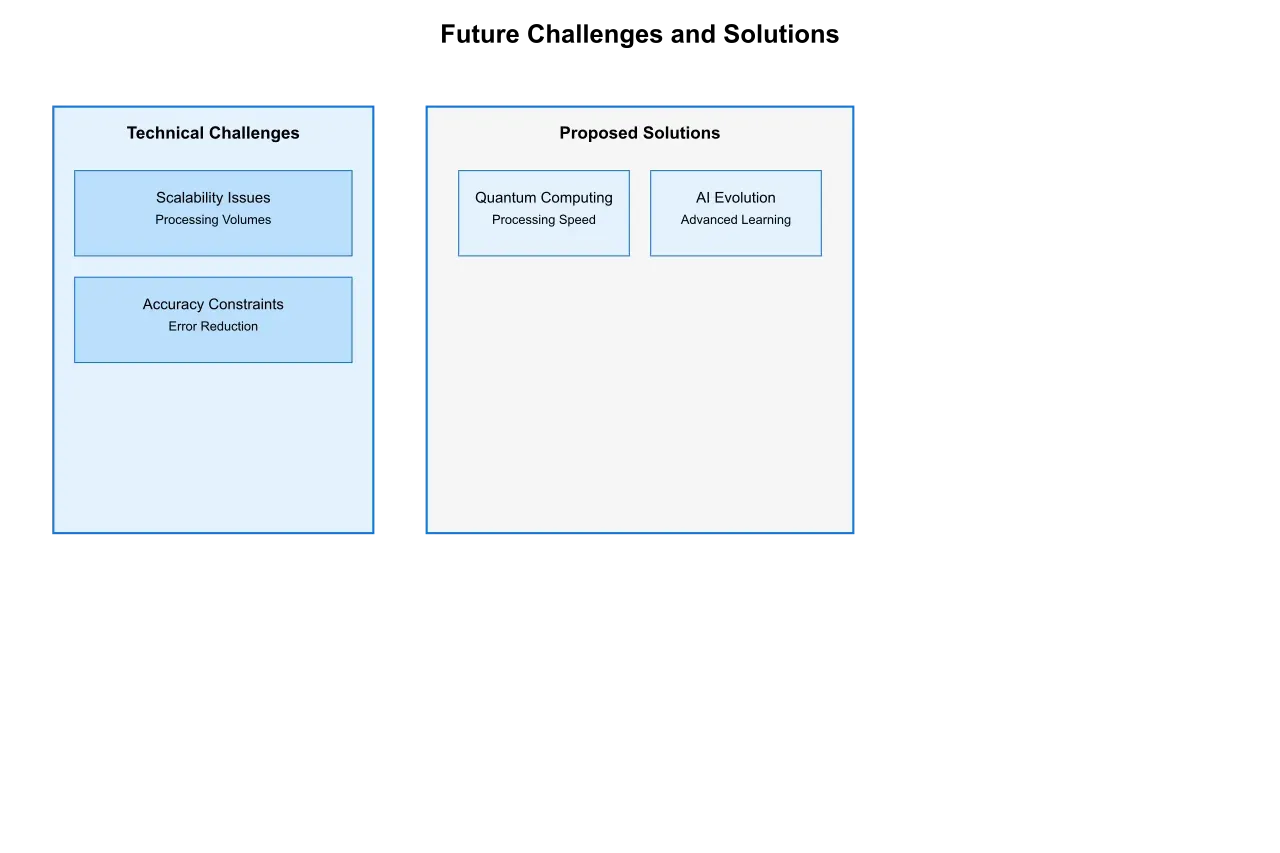
Several technical challenges remain at the forefront of development:
Handling Ambiguity: Advanced systems must resolve ambiguous table structures and relationships with higher accuracy.
Scale and Performance: Next-generation systems need to process billions of documents while maintaining sub-second response times.
Resource Optimization: Future systems must achieve higher accuracy while reducing computational resource requirements.
8. Conclusion
The evolution of table extraction and key pair processing technologies represents a fundamental advancement in document understanding and data processing. Modern systems have transformed the landscape of automated document processing, achieving previously unattainable levels of accuracy and efficiency. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated approaches that push the boundaries of what's possible in automated data extraction.